
Subscribe
eNewsletter

Ready to get certified?
Free CDCES Coach App
Download
Free Med Pocket Cards

eNewsletter

Free CDCES Coach App
Free Med Pocket Cards
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on which of the following would NOT justify providing individual DSMES instead of group DSMES. 55.1% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

After the initial assessment JM is scheduled for an individual visit instead of a group DSMES class.
According to Medicare guidelines, which of the following would NOT justify providing individual DSMES instead of group DSMES?
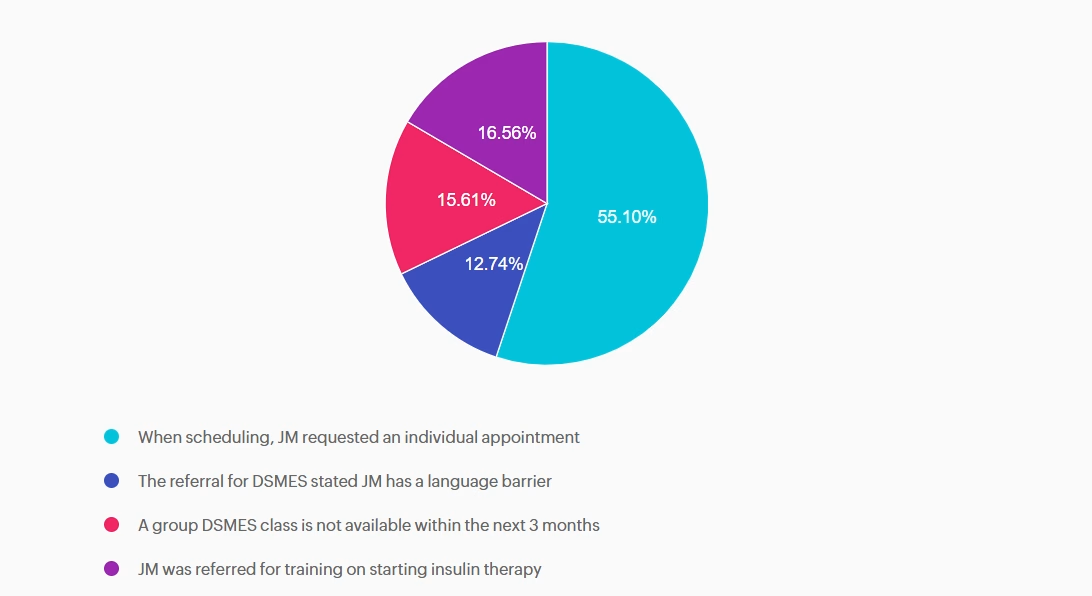
Answer A is correct: 55.1% chose this answer, “When scheduling, JM requested an individual appointment” Answer A is correct; it does NOT justify individual DSMES. Although diabetes care should be patient-centered, patient preference alone does not meet Medicare criteria for individual DSMES. Medicare requires the referring provider document justification of barriers to group learning which can include clinical, educational, or psychosocial need.
Answer B is incorrect: 12.74% chose this answer, “The referral for DSMES stated JM has a language barrier” Answer B is incorrect and does justify individual DSMES. Language barriers can significantly limit participation in group DSMES. Medicare recognizes a referral with stated language and communication needs as valid justification for an individual visit.
Answer C is incorrect: 15.61% chose this answer, “A group DSMES class is not available within the next 3 months” Answer C is incorrect and does justify individual DSMES. Medicare will approve individual DSMES if no group class is available for two months or longer from the date on the referral.
Answer D is incorrect: 16.56% chose this answer, “JM was referred for training on starting insulin therapy” Answer D is incorrect and does justify individual DSMES. A referral for initiation of insulin therapy requires individualized instruction. This can include injection technique, dose adjustment, hypoglycemia prevention, and problem-solving. Medicare considers this
an appropriate reason for individual DSMES.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!

Course credits through AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™, ACPE, ANCC, and CDR!
Get exam-ready with confidence.
Our CDCES Boot Camp Online Prep Bundle is a comprehensive, high-impact program built specifically for healthcare professionals preparing for the Certified Diabetes Care and Education Specialist (CDCES) exam who want to level-up their clinical knowledge and skills.
✔ Learn at your pace with expert-led, exam-focused content
✔ Everything you need—organized, practical, and in one place
✔ Perfect for self-directed learners who want complete, person-centered content for clinical practice and exam prep.
✔ Build knowledge, sharpen test-taking skills, and prepare with confidence—on your schedule.
Focused. Flexible. Proven.
Basic & e-Deluxe CDCES Boot Camp Bundle Includes:

Course credits through AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™, ACPE, ANCC, and CDR!
Get exam-ready with confidence.
Our comprehensive BC-ADM Online Study Programs are specifically designed for healthcare professionals who are studying for the Board Certified in Advanced Diabetes Management (BC-ADM) exam.
✔ Learn at your pace with expert-led, exam-focused content
✔ Everything you need—organized, practical, and in one place
✔ Perfect for self-directed learners who want complete, person-centered content for clinical practice and exam prep.
✔ Build knowledge, sharpen test-taking skills, and prepare with confidence—on your schedule.
Focused. Flexible. Proven.
Basic & e-Deluxe BC-ADM Boot Camp Bundle include:
Gain fresh insights, practical tools, and a deeper understanding of the latest in person-centered diabetes care. Our expert team brings the ADA Standards of Care to life—covering medications, behavior change, technology, and more!
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on TIR (Time of Range) of 89% , and what is your concern. 62.2% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

JZ is proud of their Time of Range of 89%. You notice their time below range is 7%. JZ uses a rapid-acting insulin pen 4–6 times daily to keep glucose in target range and occasionally increases the glargine dose when evening glucose is elevated.
What is your primary concern?
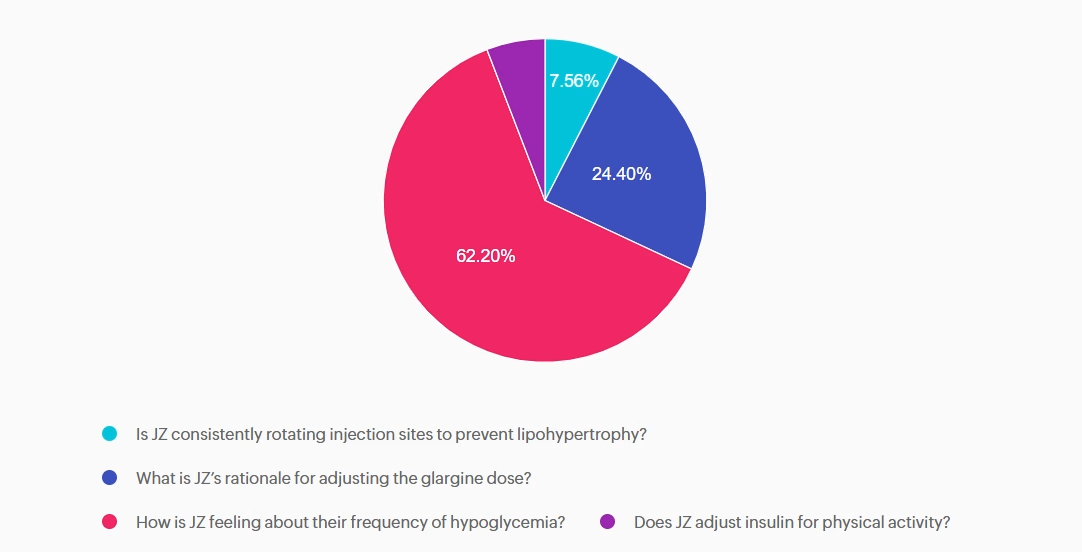
Answer A is incorrect: 7.56% chose this answer, “Is JZ consistently rotating injection sites to prevent lipohypertrophy?” Injection site rotation is important for preventing lipohypertrophy and absorption variability, but not the most immediate safety risk.
Answer B is incorrect: 24.4% chose this answer, “What is JZ’s rationale for adjusting the glargine dose?” Basal insulin is generally titrated based on overnight and fasting blood glucose levels, not reactively based on the evening glucose. This is clinically relevant, but still secondary to hypoglycemia risk.
Answer C is correct: 62.2% chose this answer, “How is JZ feeling about their frequency of hypoglycemia?” Since JZ is experiencing hypoglycemia more than the target below target range of 5%, we want to explore their feelings around their diabetes and diabetes distress.
Answer D is incorrect: 5.84% chose this answer, “Does JZ adjust insulin for physical activity?” Adjusting insulin for exercise is essential for self-management, yet the first priority is identifying whether dangerous lows are occurring.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!

Course credits through AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™, ACPE, ANCC, and CDR!
Get exam-ready with confidence.
Our CDCES Boot Camp Online Prep Bundle is a comprehensive, high-impact program built specifically for healthcare professionals preparing for the Certified Diabetes Care and Education Specialist (CDCES) exam who want to level up their clinical knowledge and skills.
✔ Basic CDCES Boot Camp – From the fundamentals, to the ADA standards, to test strategies and exam mastery! This complete exam prep includes Levels 1, 2, and 3 (30+ courses, 50+ CEs, 400+ practice questions)
✔ e-Deluxe CDCES Boot Camp – Everything in Basic PLUS the [e-Book] ADCES Certification Review Guide | 6th Edition (475+ practice questions)
✔ Mini CDCES Boot Camp – Accelerated program for experienced healthcare professionals (skips Level 1 | Diabetes Fundamentals, includes Levels 2 & 3, 20+ courses, 40+ CEs, 325+ practice questions).

Course credits through AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™, ACPE, ANCC, and CDR!
Get exam-ready with confidence.
Our comprehensive BC-ADM Online Study Programs are specifically designed for advanced level healthcare professionals who are studying for the Board Certified in Advanced Diabetes Management (BC-ADM) exam.
✔ Basic BC-ADM Boot Camp – Complete exam prep includes Levels 2, 3, and 4 (30+ courses, 50+ CEs, 400+ practice questions)
✔ e-Deluxe BC-ADM Boot Camp – Everything in Basic PLUS the ADCES Certification Review Guide E-book with an additional 475+ practice questions.
Gain fresh insights, practical tools, and a deeper understanding of the latest in person-centered diabetes care. Our expert team brings the ADA Standards of Care to life—covering medications, behavior change, technology, and more!
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on which of the following responses is the least appropriate (i.e., the WRONG thing to say) to Maria. 58.54% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

Maria, a 52‑year‑old woman with type 2 diabetes for 8 years, attends a follow‑up visit. Her A1C has risen from 7.8% to 9.2% over the past year. She reports feeling “overwhelmed” and says she didn’t want to start the medication her clinician recommended at the last visit. She explains, “I’m scared of side effects, and I feel like needing medication means I failed.”
Which of the following responses is the least appropriate (i.e., the WRONG thing to say) to Maria?
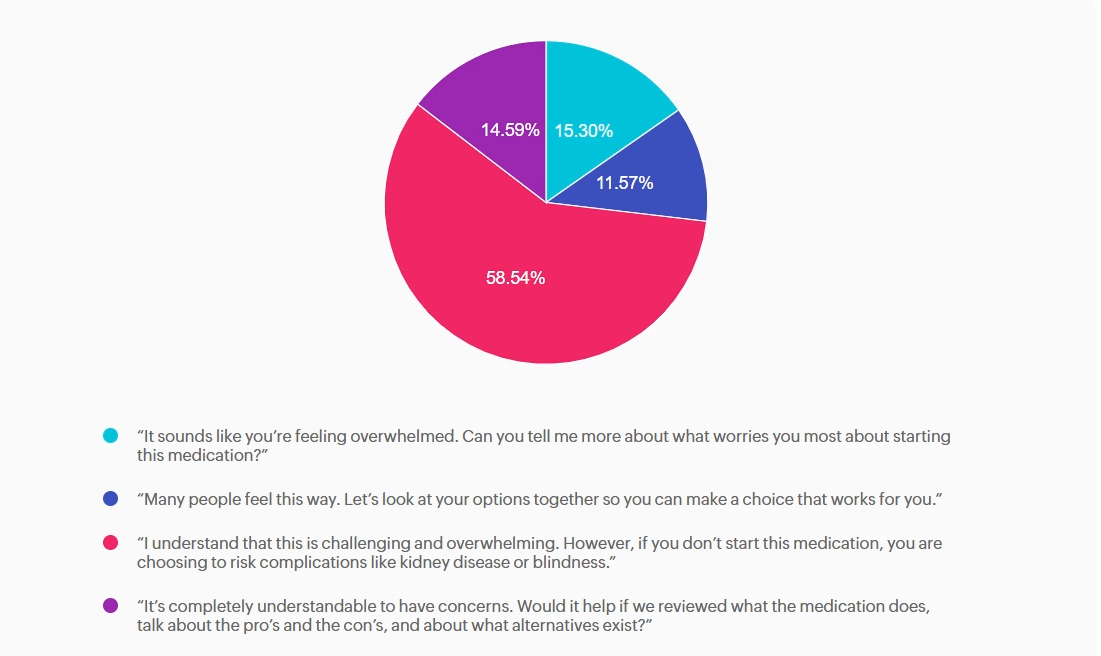
Answer A is incorrect: 15.3% chose this answer,“ It sounds like you’re feeling overwhelmed. Can you tell me more about what worries you most about starting this medication?” Appropriate — Person centered, exploratory. This response uses reflective listening and invites the patient to share her concerns. It aligns with ADA Standards of Care recommendations for collaborative communication and supports assessment of diabetes distress.
Answer B is incorrect: 11.57% chose this answer, “Many people feel this way. Let’s look at your options together so you can make a choice that works for you.” Appropriate — Normalizes feelings and supports shared decision making. This option reduces stigma by acknowledging that many people experience similar emotions. It reinforces autonomy and partnership, which are core components of effective diabetes self management support.
Answer C is correct: 58.54% chose this answer, “I understand that this is challenging and overwhelming. However, if you don’t start this medication, you are choosing to risk complications like kidney disease or blindness.” Incorrect — Stigmatizing, blaming, and fear based. This statement uses threat based language (“you are choosing to risk complications…”) and implies personal failure. It increases shame, undermines trust, and can worsen diabetes distress. It does not incorporate person first language or collaborative care or help identify barriers and personalized solutions. Oh, and it probably won’t be very successful!
Answer D is incorrect: 14.59% chose this answer, “It’s completely understandable to have concerns. Would it help if we reviewed what the medication does, talk about the pro’s and the con’s, and about what alternatives exist?” Appropriate — Validates concerns and offers. Information without pressure. This response acknowledges the patient’s emotions and provides an opening for education and shared exploration of options. It supports autonomy and reduces the sense of failure associated with medication use.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!

In this course, William H. Polonsky, PhD, CDCES, and Susan Guzman, PhD, examine the powerful role of psychosocial factors in diabetes self-management. Through innovative strategies, participants will learn how to recognize and address common barriers to effective self-care and cardiometabolic medication initiation and maintenance, while fostering respectful, stigma-free clinical encounters.
Through a collaborative and person-centered approach, the course emphasizes communication strategies that enhance motivation, build confidence, and reinforce the value of self-management. Participants will develop skills in diabetes-focused action planning, addressing medication hesitancy, and providing ongoing support and resources to sustain behavior change over time. The goal is to help clinicians make diabetes care more doable, meaningful, and effective for people living with diabetes.
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on which feature most strongly supports a diagnosis of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) rather than diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA). 59.77% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

A 32-year-old with newly discovered diabetes is brought to the emergency department with polyuria and lethargy. They have been sleeping more than usual.
Initial labs show:
Based on the following labs, which feature most strongly supports a diagnosis of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) rather than diabetes ketoacidosis (DKA)?
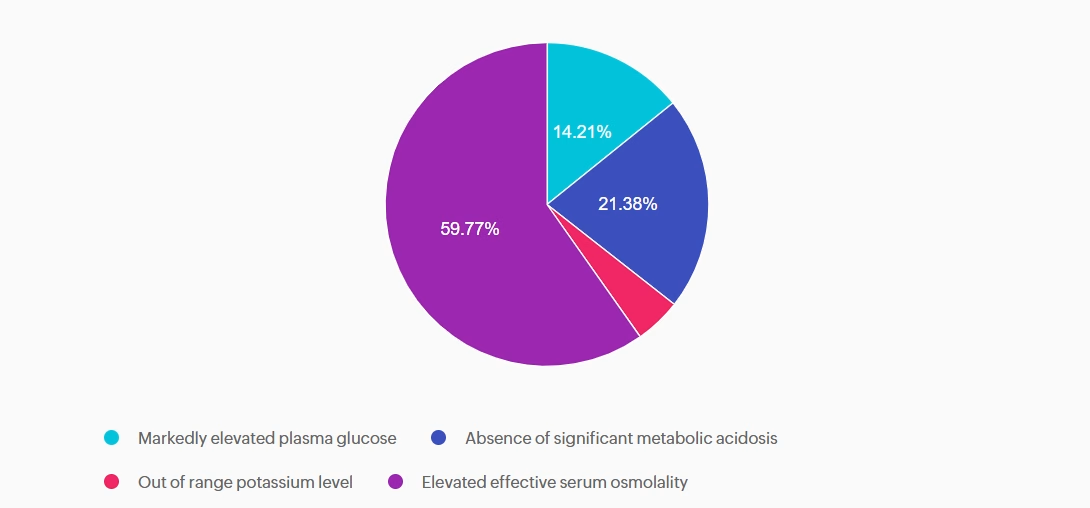
Answer A is incorrect: 14.21% chose this answer, “Markedly elevated plasma glucose.” This answer is tempting, because glucose levels do become markedly elevated with HHS. However, very high glucose levels can also occur with DKA. So this answer doesn’t differentiate between these two hyperglycemic crises.
Answer B is incorrect: 21.38% chose this answer, “Absence of significant metabolic acidosis.” This juicy answer is tempting, since with HHS there is the absence of metabolic acidosis. However, based on the question details, there is no information on pH or ketone status, so we can’t make that assumption.
Answer C is incorrect: 4.64% chose this answer, “Out of range potassium level.” The potassium level of 3.7 is within normal range and doesn’t help us differentiate between HHS and DKA.
Answer D is correct: 59.77% chose this answer, “Elevated effective serum osmolality.” YES, this is the BEST Answer. Great Job! One of the main features of HHS, is increased serum osmolality (greater than 300), due to a combination of elevated glucose and dehydration.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!

Sale Ends on February 16th, 2026!
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on recommendations for facilitating positive health behavior change, according to 2026 ADA Standards. 81.75% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

KC has type 2 diabetes, diagnosed 5 years ago. They report low physical activity, frequent sugar-sweetened beverage intake, and high stress related to work. Last A1c was 8.2%. KC reports previous advice to “exercise more and drink less soda,” but reports making minimal changes. They express interest in improving health but feels overwhelmed by where to start.
Which of the following responses best aligns with the 2026 ADA Standards of Care recommendations for facilitating positive health behavior change?
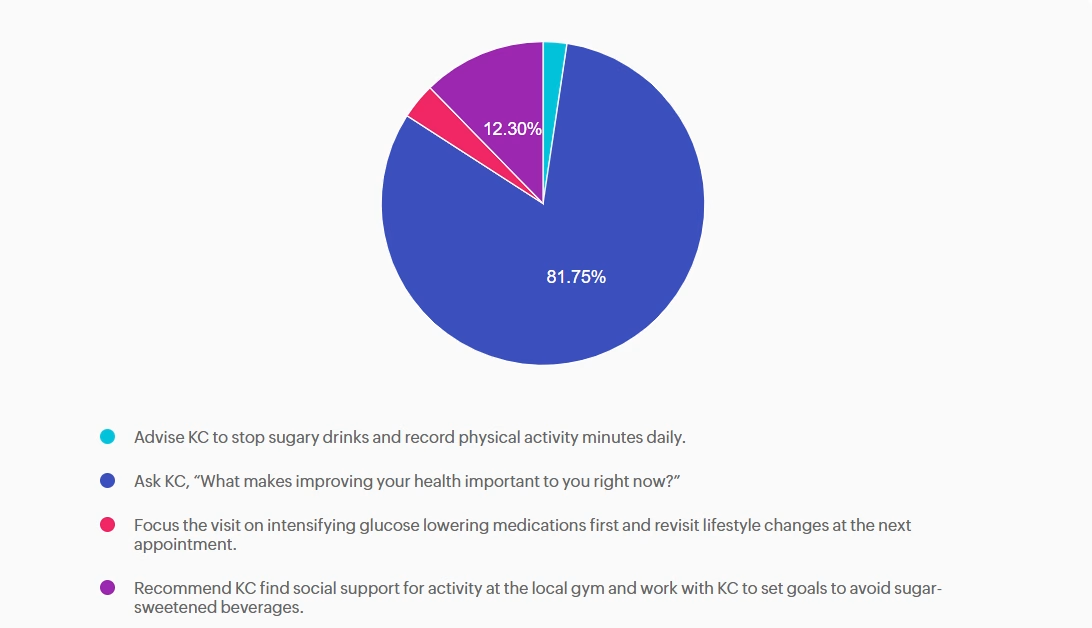
Answer A is incorrect: 2.38% chose this answer, “Advise KC to stop sugary drinks and record physical activity minutes daily.” Although the Standards of Care do recommend avoiding sugar-beverage consumption and increased activity, this answer is prescriptive and not collaborative. Simply telling the patient what to do without assessing motivation or barriers does not align with ADA recommendations for patient-centered behavior change.
Answer B is correct: 81.75% chose this answer, “Ask KC, “What makes improving your health important to you right now?”” This question is an example of a response using the strategy of motivational interviewing (MI). MI is a patient-centered counseling method that explores readiness, addresses ambivalence, helps patients identify barriers to behavior change and encourages confidence while setting goals. The 2026 ADA Standards of Care recommend using MI, along with other strategies, to help individuals with diabetes adopt sustainable lifestyle behaviors, including diet, physical activity, and stress management.
Answer C is incorrect: 3.57% chose this answer, “Focus the visit on intensifying glucose lowering medications first and revisit lifestyle changes at the next appointment.” While medication intensification may be a first step and necessary approach to support KC is their diabetes management, it fails to first address KC’s goals and desires. In addition, the 2026 ADA Standards of Care emphasize integrating behavior change support alongside pharmacologic therapy.
Answer D is incorrect: 12.3% chose this answer, “Recommend KC find social support for activity at the local gym and work with KC to set goals to avoid sugar-sweetened beverages.” While this option does consider strategies of social support and goal-setting it lacks assessment of readiness and barriers and again is a more prescriptive approach vs. collaborative approach.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!

Sale Ends on February 16th, 2026!
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on JR wanting treatment for pancreatic parasites, and what would be the best response. % of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

JR is hospitalized with influenza. They have a history of prediabetes but now have persistent glucose readings between 220–260 mg/dL and are started on basal-bolus insulin.
JR is upset and states: “I’ve been reading that pancreatic parasites can cause of diabetes. No one is treating my infection.”
What is the BEST response?
Answer A is correct: % chose this answer, “It sounds like you are worried about a parasite infection. Tell me more about what you’ve read.” Great job. A is the best answer because it uses person-centered, nonjudgmental communication, as recommended by the ADA. It avoids dismissive language and explores misinformation respectfully. It preserves the therapeutic alliance.
Answer B is incorrect: % chose this answer, “Yes. We will be treating that issue soon, but first we need to focus on your insulin doses.” Option B offers a false narrative saying that they are going to treat the parasitic infection then shifts focus to the blood glucose, without recognizing JR’s emotional distress.
Answer C is incorrect: % chose this answer, “I can see how you would be concerned, but here is no such thing as pancreatic parasites.” Option C does initially recognize the emotions but then ends with a dismissive tone, that may make JR feel defensive and unheard.
Answer D is incorrect: % chose this answer, “Sadly, prediabetes always progresses to diabetes when people are acutely ill, and you will probably be discharged on insulin therapy.” Option D completely ignores the emotional distress in addition to making assumptions that may not be true.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
Get exam-ready with confidence.
Course credits through AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™, ACPE, ANCC, and CDR!
Full accreditation details are available on the registration page

Our CDCES Boot Camp Online Prep Bundle is a comprehensive, high-impact program built specifically for healthcare professionals preparing for the Certified Diabetes Care and Education Specialist (CDCES) exam who want to level up their clinical knowledge and skills.

This evidence-based study bundle is a comprehensive BC-ADM Boot Camp designed for advanced-level healthcare professionals preparing for the Board Certified in Advanced Diabetes Management (BC-ADM) exam and will also provide you with state-of-the-art information to level up your clinical practice.

Join national experts including Dr. Diana Isaacs (Cleveland Clinic), Beverly Thomassian (30+ years of experience), and Christine Craig for high-impact, virtual learning—no travel required.
✔ Learn from National Experts — Anywhere
Get the same expert-level instruction you’d receive in person, delivered live to your home or office.
✔ Interactive & Flexible
Walk away with tools you can apply immediately in clinical practice or while preparing for CDCES or BC-ADM exams. From insulin dosing protocols to behavior change strategies that work in the real world—this content bridges theory and practice.

For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on J.C.’s family history and lab work, and what it reveals. 80.92% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

J.C. is a ten-year-old female with a family history of type 1 diabetes. Her 7-year-old brother was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes two years ago. J.C. has no complaints and reports feeling well. She enjoys playing sports, including basketball and soccer. Her current BMI is 22.1 (93rd percentile for age). She denies any polydipsia, polyuria, or polyphagia. Her lab work demonstrates a fasting blood sugar of 71 mg/dL, an A1c of 5.0%, normal kidney function, and normal electrolytes. Her diabetes autoantibody panel shows positive glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and islet antigen 2 (IA-2) antibodies, negative zinc transporter 8 (ZnT8) antibodies, and negative insulin antibodies.
What does her lab work reveal?
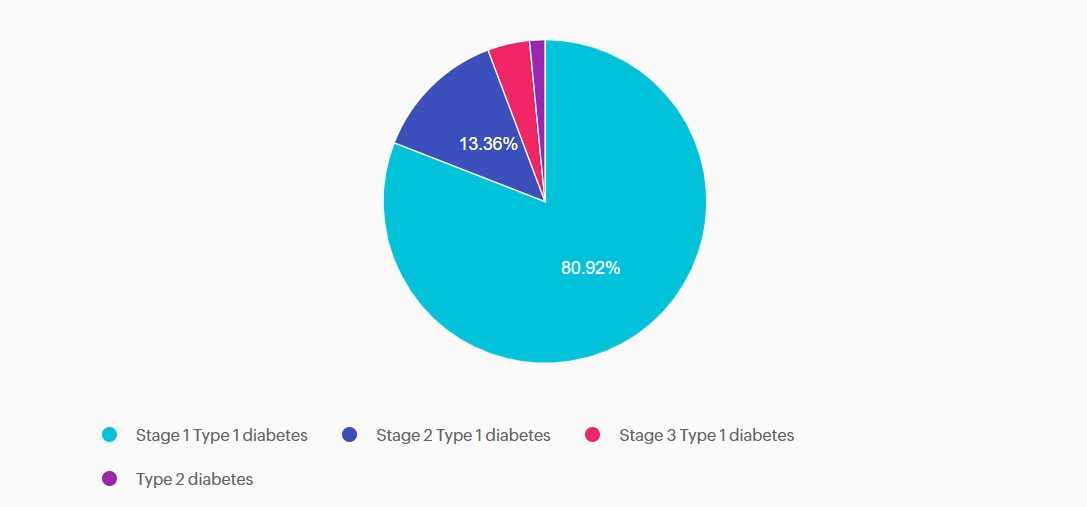
Answer A is correct: 80.92% chose this answer, “Stage 1 Type 1 diabetes.” J.C. has stage 1 type 1 diabetes. She has two positive autoantibodies and normoglycemia.
Answer B is incorrect: 13.36% chose this answer, “Stage 2 Type 1 diabetes.” J.C. still has normoglycemia. Stage 2 type 1 diabetes is characterized by positive autoantibodies and dysglycemia (Impaired fasting glucose, Impaired glucose tolerance, or elevated A1c over 5.7% or 10% increase in A1C).
Answer C is incorrect: 4.2% chose this answer, “Stage 3 Type 1 diabetes.” J.C. does not have lab work confirming diabetes by the standard diagnostic criteria, and she is asymptomatic. Stage 3 type 1 diabetes is characterized by overt hyperglycemia and symptoms of diabetes with autoimmunity present.
Answer D is incorrect: 1.53% chose this answer, “Type 2 diabetes.” J.C. does not have type 2 diabetes. She does have a BMI in the overweight category, but she does not have hyperglycemia. She also has positive autoantibodies associated with type 1 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is not immune-mediated.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!

Welcome to our selection of comprehensive CDCES Boot Camp Online Prep Bundles that are specifically designed for healthcare professionals who are studying for the Certified Diabetes Care and Education Specialist (CDCES) exam.
Course credits through AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™, ACPE, ANCC, and CDR!
We offer a selection of prep bundles to meet everyone’s needs! See the descriptions below to review what is included in each option.
CDCES Boot Camp | Basic Exam Prep Bundle: This option is perfect for someone who wants just the Online Courses and materials all in one place, our Online University. This bundle includes Levels 1, 2, and 3 & Toolkits which equates to over 30 courses, 50 CEs/CPEUs, and 400+ online practice questions.
CDCES Boot Camp | e-Deluxe Exam Prep Bundle: This bundle has all of the courses from the Basic Bundle, along with the ADCES Certification Review Guide Practice Questions e-book with 400+ practice questions.
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on what needs to be included in the initial screening for PAD, according to ADA Standards. 56.08% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is significantly underdiagnosed. While PAD affects around 8.5 million Americans and prevalence rises with age (up to 20% over 60), only 10-20% are clinically diagnosed, highlighting a major gap in awareness and screening.
According to the ADA Standards, what needs to be included in the initial screening for PAD?
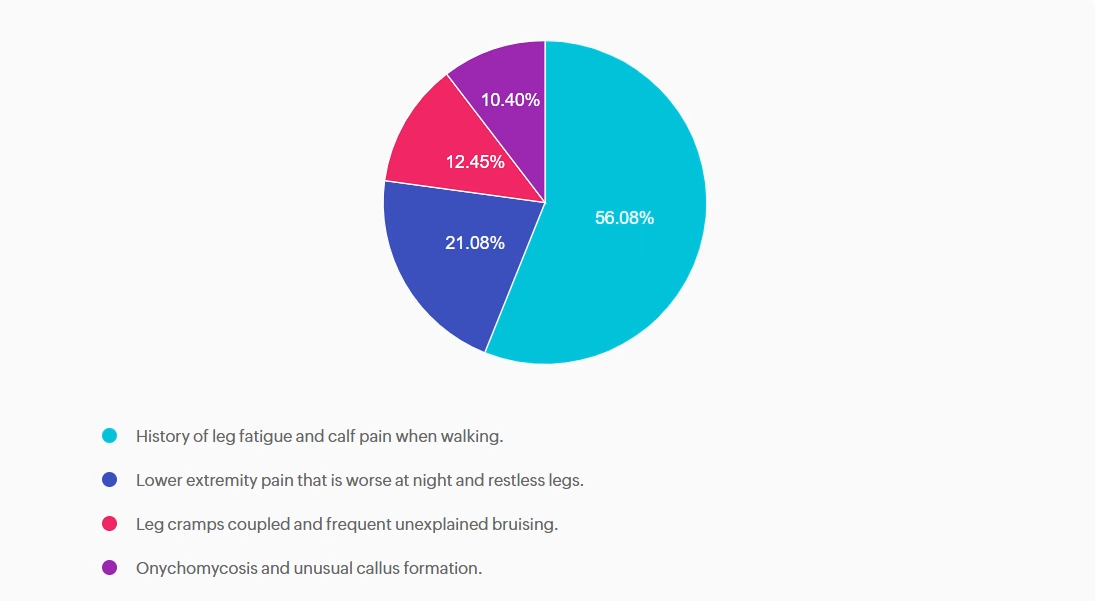
Answer A is correct: 56.08% chose this answer, “History of leg fatigue and calf pain when walking.” YES, great job. According to the ADA, if a person presents with leg fatigue and intermittent claudication, a more detailed screening for peripheral arterial disease (PAD) and poor arterial circulation is warranted.
Answer B is incorrect: 21.08% chose this answer, “Lower extremity pain that is worse at night and restless legs.” People experiencing neuropathy will complain of leg pain and burning that is worse when resting. People with PAD complain of leg and buttock pain when walking due to diminished circulation and poor blood flow to muscles that is relieved with rest.
Answer C is incorrect: 12.45% chose this answer, “Leg cramps coupled and frequent unexplained bruising.” Only part of this answer is correct. Although leg cramps or calf pain can occur with PAD, there is not direct association with frequent unexplained bruising.
Answer D is incorrect: 10.4% chose this answer, “Onychomycosis and unusual callus formation.” People with diabetes do have an increased risk of toenail infections and onychomycosis, but this is not associated with the manifestations of PAD.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!