For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on steatosis treatment according to ADA. 57% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

Question: Up to 70% of people with diabetes have steatosis. Those at higher risk of moving to steatohepatitis include individuals with prediabetes and diabetes who also have cardiometabolic risk factors.
According to ADA Standards, which of the following is an accurate statement regarding treatment of liver disease in diabetes?
Answer Choices:
- GLP-1 Receptor agonists help with weight loss but do not improve steatosis.
- Pioglitazone therapy is indicated for individuals with steatohepatitis.
- Avoid insulin therapy in individuals with steatosis and advanced cirrhosis.
- Statin therapy is not effective at LDL lowering for individuals with steatosis.
Common Native Plants in the U.S.
Getting to the Best Answer
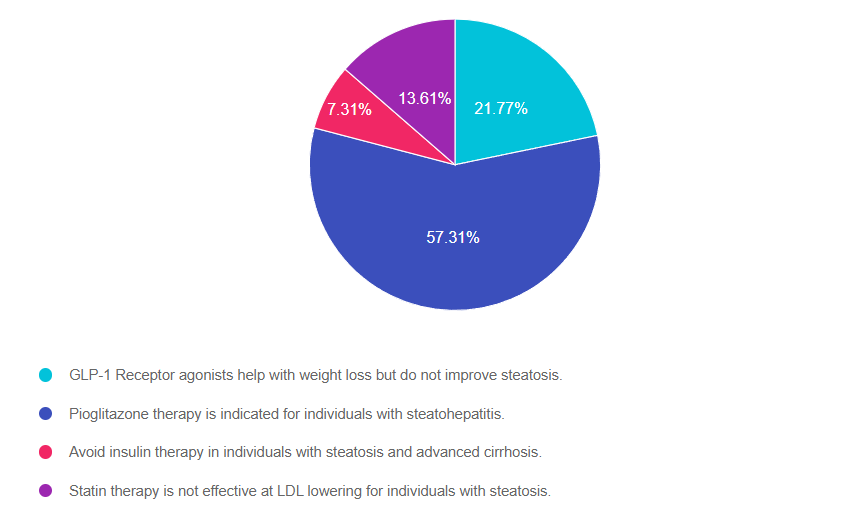
Answer 1 is incorrect. 21.77% chose this answer. “GLP-1 Receptor agonists help with weight loss but do not improve steatosis.” This juicy answer is tempting, but it is not the best answer. GLP-! RA’s, lower blood glucose levels and they also promote significant weight loss. This results in less glucose toxicity and a decrease in hepatic fat storage. Plus, they decrease the risk of cardiovascular disease which is co-associated with steatosis. See our Meds for Liver Disease Blog for more info.
Answer 2 is correct. 57.31% of you chose this answer. “Pioglitazone therapy is indicated for individuals with steatohepatitis.” Yes, this is the best answer. Pioglitazone (Actos) reduces blood glucose, and several studies demonstrate it is an effective treatment for steatosis and steatohepatitis. It also reduces the progression of fibrosis and cardiovascular risk. Since pioglitazone can cause fluid retention and weight gain, avoid using it in those with heart failure. See our Meds for Liver Disease Blog for more info.
Answer 3 is incorrect. About 7.31% of respondents chose this. “Avoid insulin therapy in individuals with steatosis and advanced cirrhosis.” With advanced cirrhosis, many of the oral medications may not be safe to use. The ADA recommends using insulin therapy, since it is safe and effective for people experiencing cirrhosis. Since people with cirrhosis are at higher risk of hypoglycemia, close monitoring of glucose levels is recommended. See our Meds for Liver Disease Blog for more info.
Finally, Answer 4 is incorrect. 13.61% chose this answer. “Statin therapy is not effective at LDL lowering for individuals with steatosis.” Lipid-lowering and antihypertensive meds need to be prescribed in people with steatosis as indicated. Statins are safe in individuals with steatohepatitis but avoid their use in those with decompensated cirrhosis. See our Meds for Liver Disease Blog for more info.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
Want to learn more about this question?
Join us live on March 27th, 2024 for our
Critical Assessment in Diabetes Care | Fine-Tuning Diabetes Detective Skills
Level 2 | Standards of Care Intensive

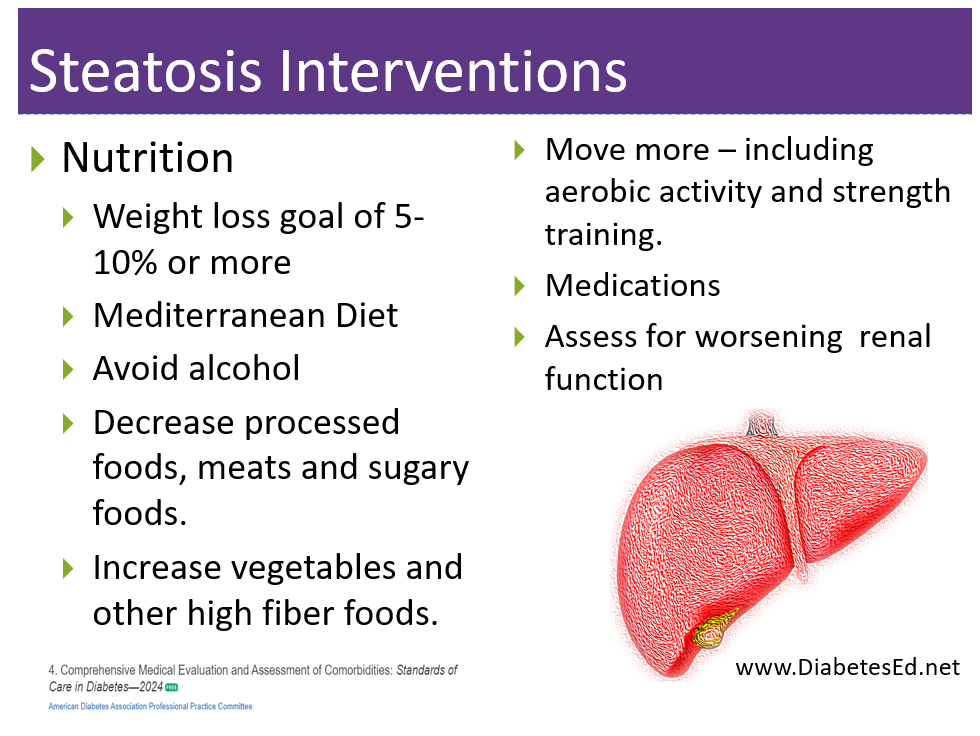
This course integrates the American Diabetes Association’s (ADA) Standard of Care on elements of a comprehensive medical assessment (Standard 4) of the individual living with prediabetes, diabetes, or hyperglycemia. Through case studies & real-life situations, we discover often hidden causes of hyperglycemia & other complications, such as liver disease, sleep apnea, pancreatitis, autoimmune diseases, fractures, & more. We delve into therapy for complicated situations & discuss management strategies for other conditions associated with hyperglycemia such as Cystic Fibrosis, & Transplants.
Objectives:
- Identify common yet often underdiagnosed complications associated with type 1 & type 2 diabetes.
- State strategies to identify previously undiscovered diabetes complications during assessments.
- Discuss links between hyperglycemia & other conditions including transplant, cystic fibrosis, & liver disease.
Intended Audience: These courses are knowledge-based activities designed for individual or groups of diabetes educators, including RNs, RDs, Pharmacists, Nurse Practitioners, Clinical Nurse Specialists, Physician Assistants, and other health care providers interested in enhancing their diabetes assessment skills and preparing for certification.
Instructor: Beverly Thomassian RN, MPH, CDCES, BC-ADM is a working diabetes specialist and a nationally recognized diabetes expert.
Sign up for Diabetes Blog Bytes – we post weekly Blog Bytes that are informative and FREE! Every week we post one exam practice Question of the Week and Rationale of the Week. Sign up below!
Accreditation: Diabetes Education Services is an approved provider by the California Board of Registered Nursing, Provider 12640, and our CPEU courses have received Prior Approval* from the Commission of Dietetic Registration (CDR), Provider DI002. Since our CPEU courses received Prior approval* from the CDR, these CPEU courses satisfy the CE requirements for the CDCES /BC-ADM regardless of your profession!
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the certification exam. CBDCE and ADCES do not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the CDCES or BC-ADM exams, except for those published by CBDCE & ADCES.