For our August 10th Question of the Week, 37% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to “take a closer look” at this question and determine strategies to choose the best response.
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer below: Answer Question
Question 1: AL is 24 with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes. AL is very worried about going blind because an Aunt with Type 1 diabetes lost her vision due to living with type 1 diabetes.
Which of the following matches the ADA guidelines for diabetes eye care?
- An eye examination is recommended before pregnancy.
- Get eye exam immediately at type 1 diabetes diagnosis, then yearly thereafter.
- If no retinopathy found on initial exam, refer to trained retinal expert for thorough exam.
- Only trained ophthalmologist can screen for type 1 diabetes eye disease.
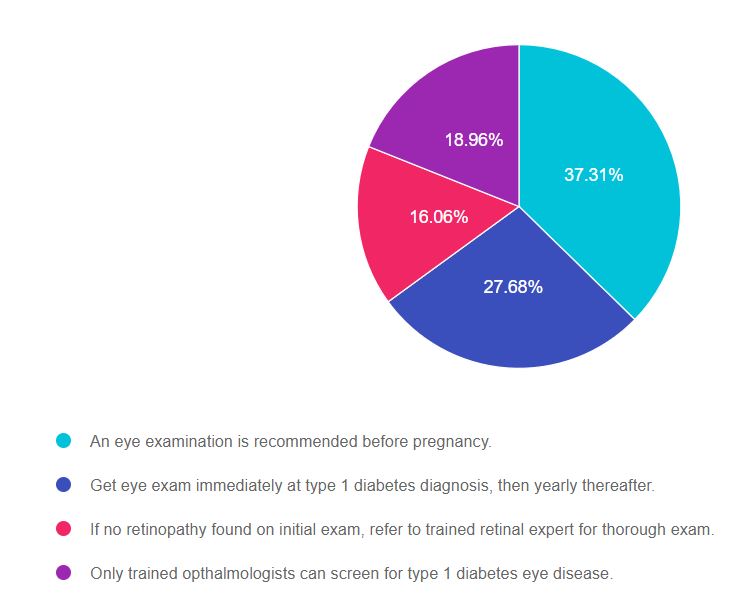
As shown above, the most common choice was option 1, the second most common answer was option 2, then option 4, and finally option 3.
Getting to the Best Answer
If you are thinking about taking the certification exam, the content of this practice test question will set you up for success. Don’t forget to leverage your common sense and vast health care knowledge to get the best answer for specialty topics like microvascular disease. Be familiar with screening guidelines for eye disease as listed in the ADA Standards of Care on Microvascular health and treatment options. We also invite you to join our webinar (see below). You got this, Coach Beverly
Answers & Rationale
Answer 1 is correct, 37.31% chose this answer, “An eye examination is recommended before pregnancy.” Great Job! Yes, this is the best answer. All people living with diabetes considering pregnancy need to get a baseline eye exam to evaluate retinal health. In addition, the ADA Standards recommend eye exams each trimester of pregnancy and after birth to monitor retinal changes.
Answer 2 is incorrect, 27.68% of you chose this answer, “Get eye exam immediately at type 1 diabetes diagnosis, then yearly thereafter.” This is the juicy answer. According to the ADA Standards for people with type 1 diabetes, they need an eye exam within in 5 years of diagnosis, then an eye exam every 1-2 years. The reason they don’t require an immediate eye exam is because type 1 diabetes is quickly identified and this short span of hyperglycemia does not increase risk of retinopathy. The reason we check people with type 2 eyes immediately, is because they could have had diabetes for an average of 6 years before diagnosis, allowing for the possibility of undetected eye damage.
Answer 3 is incorrect, 16.06% of you chose this answer, “If no retinopathy found on initial exam, refer to trained retinal expert for thorough exam.” ‘All people with diabetes do not need to be referred to a retinal expert. An ophthalmologist or optometrist can screen for type 1 diabetes eye disease. If retinopathy is discovered, depending on the severity, they may advise referral to a retinal specialist as needed.
Answer 4 is incorrect, 18.96% of you chose this answer “Only a trained ophthalmologists can screen for type 1 diabetes eye disease.” An ophthalmologist or optometrist can screen for type 1 diabetes eye disease. Programs that use retinal photography (with remote reading or use of a validated assessment tool) are also appropriate screening strategies for diabetes retinopathy. Such programs need to provide pathways for timely referral for a comprehensive eye examination when indicated.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
Want to learn more about this topic?
Join us for our
Level 2 | Microvascular Complications, Eye Kidney, & Nerve Disease Standards | 1.5 CEs
This course provides you with the need-to-know information regarding the microvascular complications of diabetes. We start with a brief overview of the pathophysiology and clinical manifestations then sum up with prevention strategies and screening guidelines. This straight-forward program will provide you with information you can use in your clinical setting and also provides critical content for the diabetes educator exam.
Objectives:
- Eye, kidney and nerve disease
- Modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors for diabetes complications
- Screening guidelines and prevention strategies.
Enroll Now | 1.5 CEs | $29
Join us for our
Level 2 | Setting up a Successful DSME Program Standards | 1.5 CEs

This course provides you with a succinct overview of the latest standards for Diabetes Self-Management Education (DSME) and Support Programs. If you are taking the CDCES Exam or considering setting up a DSME program, this program is designed for you. We review the 10 standards and provide strategies on implementation. In addition, we discuss Medicare Reimbursement and covered benefits. This course provides insights into the exam philosophy and also highlights critical content areas.
Objectives:
- The steps involved in setting up a Diabetes Program
- List program essentials
- Discuss marketing strategies for success
See Full Calendar for upcoming webinars and events.
Can’t make it live? All paid registrants are guaranteed access to the video presentation, handouts and podcasts.
Sign up for Diabetes Blog Bytes – we post one daily Blog Byte from Monday to Friday. And of course, Tuesday is our Question of the Week. It’s Informative and FREE! Sign up below!
[yikes-mailchimp form=”1″]Accreditation: Diabetes Education Services is an approved provider by the California Board of Registered Nursing, Provider 12640, and Commission on Dietetic Registration (CDR), Provider DI002. Since these programs are approved by the CDR it satisfies the CE requirements for the CDCES regardless of your profession.*
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the CDCES exam. CBDCE does not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the CDCES exam, except for those published by CBDCE.