For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on gestational diabetes & medication. A whopping 70% of respondents chose the best answer – great job. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question
Question: AR has PCOS and type 2 diabetes and is in shock because they just discovered they are 6 weeks pregnant. AR takes metformin 1000mg BID plus empagliflozin (Jardiance) 25 mg and their most recent A1C is 8.6%.
Which of the following actions do you recommend?
Answer Choices:
- Stop empagliflozin
- Stop metformin, keep empagliflozin
- Stop metformin and empagliflozin, start insulin.
- Stop empagliflozin, start a GLP-1 inhibitor
Getting to the Best Answer
If you are thinking about taking the certification exam, this practice test question will set you up for success. Test writers anticipate possible answers based on the details in the question. They will wave those “juicy answers” right under your nose. Your job is to weed through the particulars, pluck out the most important elements and choose the BEST answer.
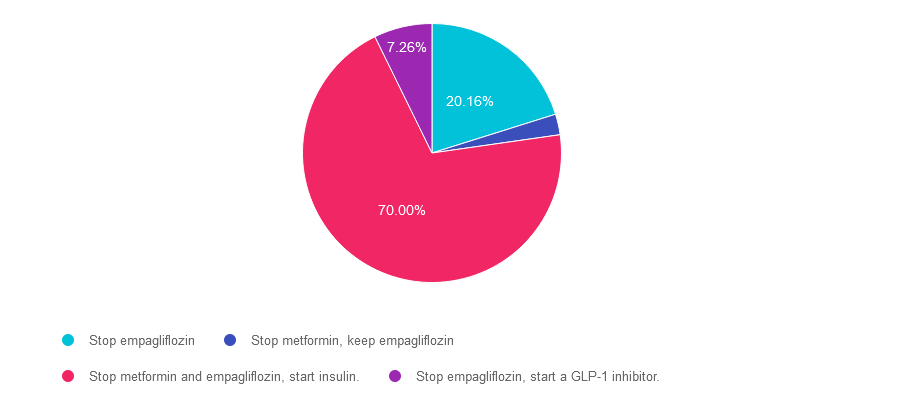
Answer 1 is incorrect. 20.16% chose this answer. “Stop empagliflozin.” It is true that empagliflozin and all SGLT-2’s are not indicated during pregnancy. However, there is a better answer given that her A1C of 8.6% is above the pregnancy target of less than 6.5%.
Answer 2 is incorrect. 2.58% of you chose this answer. “Stop metformin, keep empagliflozin.” Empagliflozin and all SGLT-2’s are contraindicated during pregnancy, so this answer is not the best choice.
Answer 3 is correct. About 70% of respondents chose this. “Stop metformin and empagliflozin, start insulin.” GREAT JOB. Given that her A1C of 8.6% is above the pregnancy target of less than 6.5%, insulin absolutely needs to be started to get glucose to goal. According to the ADA Standards, the provider may opt to continue the metformin treatment for PCOS for the first trimester But given the urgent need to get blood glucose to target, this individual will be most effectively managed with a combination of nutrition therapy and insulin.
Finally, Answer 4 is incorrect. 7.26% chose this answer. “Stop empagliflozin, start a GLP-1 inhibitor.” Yes, we need to stop empagliflozin since all SGLT-2’s are contraindicated during pregnancy. However, GLP-1 Inhibitors are also contraindicated during pregnancy, so this answer is incorrect.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
Want to learn more about this question? Enroll in our
Level 2 | Pregnancy & Diabetes | 1.5 CEs

Pregnancy with diabetes is confronted with a variety of issues that require special attention, education, & understanding. This course reviews those special needs while focusing on Gestational Diabetes & Pre-Existing Diabetes. Included are the most recent diagnostic criteria, management goals, & prevention of complications during pregnancy. This is a helpful review for Certification Exams & those who want more information on people who are pregnant & live with diabetes.
Objectives:
- List three issues that affect pregnancy with diabetes.
- Describe the unique attributes of pre-existing diabetes in pregnancy & gestational diabetes.
- State the diagnostic criteria & management goals for gestational diabetes.
- Potential short-term & long-term complications of fetal exposure to hypoglycemia.
- Prevention measures to keep mother & baby healthy.
Intended Audience: A great course for healthcare professionals seeking to enhance their knowledge of the issues surrounding pregnancy and diabetes and appropriate care to improve outcomes.
Level 2 | Hospitals & Hyperglycemia | 1.5 CEs

Research clearly demonstrates the importance of glucose control during hospitalization to improve outcomes not only in the inpatient setting but after discharge. This course reviews the evidence that supports inpatient glucose control & outlines practical strategies to achieve targets in the inpatient setting. We incorporate the latest American Diabetes Association’s (ADA) Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes & provide links to resources & inpatient management templates.
Objectives:
- Describe the impact of hyperglycemia in the hospital setting.
- Discuss the importance of inpatient glucose control.
- List three strategies to get glucose to goal in the hospital setting.
Intended Audience: A great course for healthcare professionals seeking strategies to manage and improve inpatient diabetes care.
Don’t worry if you can’t make it live. Your registration guarantees access to the recorded version in the Online University.
All hours earned count toward your CDCES Accreditation Information
Sign up for Diabetes Blog Bytes – we post one daily Blog Byte from Monday to Friday. And of course, Tuesday is our Question of the Week. It’s Informative and FREE! Sign up below!
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the CDCES exam. CBDCE does not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the CDCES exam, except for those published by CBDCE.