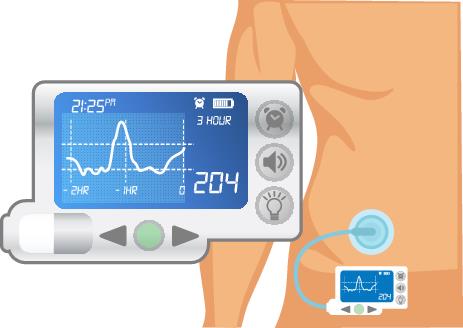
A three-year long study showed real time continuous glucose monitoring (rtCGM) was associated with lower A1c levels in people with type 1 diabetes, whether the participants used pumps or multiple daily injections.
In the study, participants checked glucose levels using CGM or fingersticks four times per day.
Only the real time CGM group had improvements in time-in-range and reduced time below range, regardless of whether they used an insulin pump or injections.
Also, fewer participants using real time CGM experienced severe hypoglycemia.
This three-year study came from the Comparison of Different Treatment Modalities for Type 1 Diabetes Including Sensor-Augmented Insulin Regimens (COMISAIR). The group still advocates for individualization of treatment, but emphasizes what an important difference incorporating real time CGM makes.
Jan Soupal presented the study findings at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes 2019 Annual Meeting in the Czech Republic. Soupal noted that CGM can be coupled with multiple daily injections for those who prefer to only have one device on their body or worry about accessibility and affordability.
Read the full study details here.

Want more valuable CGM info for the test?
Check out our Technology Toolkit! Two fantastic courses included for a total of 3 CEs:
- Tech 101 – Pumps and Sensors Update and Overview and
- Tech 102 – Insulin Pump Calculations: From Basal to Square Bolus
Sign up for Diabetes Blog Bytes – we post one daily Blog Byte from Monday to Friday. And of course, Tuesday is our Question of the Week. It’s Informative and FREE! Sign up below!
[yikes-mailchimp form=”1″]