Rationale of the Week | Best Treatment for H. pylori?

For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on treating H. pylori. 78.42% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question
Question: JR is 50, has type two diabetes, and was referred to G.I. due to six months of stomach pain, intestinal, bloating, and generalized G.I. discomfort. Since they were due for their colonoscopy, the doctor also ordered an upper endoscopy to biopsy the esophagus, stomach and duodenum for any abnormalities.
The biopsy revealed that JR had moderate chronic gastritis and an H. pylori infection. JR wants to learn more about H. pylori infection.
Which of the following statements are accurate?
Answer Choices:
- Since H. pylori is found in about half the population, it is a normal finding, and there is no need for treatment.
- Treatment includes double antibiotic therapy and a medication to decrease gastric acidity.
- The preferred treatment is the consumption of prebiotics and probiotics to increase bacterial diversity.
- Most people with H. pylori infection experience stomach cancer within the next 20 years.

Getting to the Best Answer
If you are thinking about taking the certification exam, this practice test question will set you up for success. Test writers anticipate possible answers based on the details in the question. They will wave those “juicy answers” right under your nose. Your job is to weed through the particulars, pluck out the most important elements and choose the BEST answer.
Answer 1 is incorrect. 5.27% chose this answer. “Since H. pylori is found in about half the population, it is a normal finding, and there is no need for treatment.” It is true that 50% of people worldwide house H. plyori in their stomach. However, in a small percentage of human hosts, this little bacteria “goes rogue” and causes gastritis, loss of stomach mucous lining, peptic ulcers and can be associated with some stomach cancers.
Answer 2 is correct. 78.42% of you chose this answer. “Treatment includes double antibiotic therapy and a medication to decrease gastric acidity.” YES, GREAT JOB. According to the Cleveland Clinic, 2 antibiotics and a proton pump inhibitor are prescribed to address H. pylori infections.
Antibiotics: Among the common choices are amoxicillin, clarithromycin (Biaxin®), metronidazole (Flagyl®) and tetracycline.
Proton pump inhibitor: Commonly used proton pump inhibitors include lansoprazole (Prevacid®), omeprazole (Prilosec®), pantoprazole (Protonix®), rabeprazole (Aciphex®) or esomeprazole (Nexium®).
Answer 3 is incorrect. About 13.84% of respondents chose this. “The preferred treatment is the consumption of prebiotics and probiotics to increase bacterial diversity.” Consuming prebiotics and probiotics are a recommended adjunctive therapy to antibiotics and a proton pump inhibitor. However, current evidence does not support pre and probiotics as the only treatment.
Finally, Answer 4 is incorrect. 2.47% chose this answer.” Most people with H. pylori infection experience stomach cancer within the next 20 years.” There is a slightly increased risk (~5%) of stomach cancer for those with H. plyori infection, especially if the H. pylori isn’t treated or if there is a family history of stomach cancer. This answer is suspicious because of the extreme statement that “Most” people get cancer from this bacteria gone rogue.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
Want to learn more about the GI System and Diabetes?
From the Gut to the Butt – Exploring the GI System FREE Webinar
Now Recorded & Ready to Watch

Coach Bev invites you to join this 60 minute webinar that covers gastrointestinal health from top to bottom. Topics include; fatty liver disease diagnosis and treatment, intestinal complications associated with diabetes, keeping the microbiome healthy, and more. Join us to explore the magnificent wonders of diabetes and the gut.
Getting to the Gut Topics:
- From the Mouth to Intestines: Periodontal disease, Gastroparesis, Fatty liver disease, pancreas disorders
- Intestine as an Endocrine Organ & Bacterial Host
- NASH Treatment Options including lifestyle and pharmacotherapy
- State the relationship between gut health, microbiome and diabetes and inflammation
- Describe 3 strategies to get our microbiome back to better health.
Can’t make it live? No worries. We will send post the recorded version to the Online University within 24 hours of the broadcast
Instructor: Beverly Thomassian RN, MPH, CDCES, has been Board Certified in Advanced Diabetes Management for over 20 years. She is an Associate Clinical Professor at UCSF, a working educator, and a nationally recognized diabetes expert. She has a Master’s Degree in Public Health from UCLA, with a focus on behavioral health and education.
All hours earned count toward your CDCES Accreditation Information
Diabetes and the Gut – ADCES Hawaii Annual Conference with Coach Beverly
October 27, 2023 – Join us in beautiful Oahu & Earn 6.5 CEs
ADCES Hawaii Chapter & Coach Bev invite you to join this class that covers gastrointestinal health from top to bottom. Topics include; fatty liver disease diagnosis and treatment, intestinal complications associated with diabetes, keeping the microbiome healthy, and more. Join us to explore the magnificent wonders of diabetes and the gut.
Location: Honolulu Country Club, 1689 Ala Pu’umalu Street, Honolulu, HI
CEs: 6.5 CEs for physicians, nurses, pharmacists, physician assistants, dieticians & social workers.
Sign up for Diabetes Blog Bytes – we post one daily Blog Byte from Monday to Friday. And of course, Tuesday is our Question of the Week. It’s Informative and FREE! Sign up below!
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the diabetes certification exams. CBDCE & ADCES does not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the certification exams, except for those published by CBDCE & ADCES.
Rationale of the Week | G-POEM for Gastroparesis?

For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on reviewing insulin dosing adjustments. 69% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question
Question: JR lives with type 1 diabetes and severe gastroparesis, despite maintaining an A1C of less than 7% for the past few years. The endocrinologist referred JR to a GI specialist, who recommended a surgical procedure called a Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy, G-POEM, to address JR’s longstanding gastroparesis.
JR asks what you think about this intervention. What is the best response?
Answer Choices:
- It sounds like you are worried about the effectiveness and risks of this procedure. Is that right?
- Tell me more about what your GI doctor told you about this procedure.
- I know you are frustrated, but the primary treatment for gastroparesis is low fiber meals.
- Usually, gastroparesis improves as your A1C reaches target so I would wait and see if things improve.

Getting to the Best Answer
If you are thinking about taking the certification exam, this practice test question will set you up for success. Test writers anticipate possible answers based on the details in the question. They will wave those “juicy answers” right under your nose. Your job is to weed through the particulars, pluck out the most important elements and choose the BEST answer.
Answer 1 is incorrect. 28.90% chose this answer. “It sounds like you are worried about the effectiveness and risks of this procedure. Is that right?” This tempting answer is not the best answer since JR never states that they are worried about the effectiveness of the G-POEM. Instead they just want to see what the Diabetes Care and Education Specialist thinks about this procedure. When in doubt, re-examine the key intent of the question.
Answer 2 is correct. 69.27% of you chose this answer. “Tell me more about what your GI doctor told you about this procedure.” YES, this is the BEST answer. Great job. By asking what JR knows about the procedure, we provide JR an opportunity to share their knowledge and assess areas of concern. In addition, we may let JR know that we haven’t heard of this procedure, but we will look into it.
Answer 3 is incorrect. About 0.92% of respondents chose this. “I know you are frustrated, but the primary treatment for gastroparesis is low fiber meals.” It is true that we recommend low fiber meals for gastroparesis, but JR was asking about a procedure not meal planning.
Finally, Answer 4 is incorrect. 0.92% chose this answer. “Usually, gastroparesis improves as your A1C reaches target so I would wait and see if things improve.” It is true that the stomach is better at moving its’ content forward when blood sugars are closer to target most of the time. But, sometimes, despite having an A1C on target, severe autonomic neuropathy interferes with stomach propulsion past the pyloric sphincter.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
Want to learn more about the GI System and Diabetes?
From the Gut to the Butt – Exploring the GI System FREE Webinar
Now Recorded & Ready to Watch

Coach Bev invites you to join this 60 minute webinar that covers gastrointestinal health from top to bottom. Topics include; fatty liver disease diagnosis and treatment, intestinal complications associated with diabetes, keeping the microbiome healthy, and more. Join us to explore the magnificent wonders of diabetes and the gut.
Getting to the Gut Topics:
- From the Mouth to Intestines: Periodontal disease, Gastroparesis, Fatty liver disease, pancreas disorders
- Intestine as an Endocrine Organ & Bacterial Host
- NASH Treatment Options including lifestyle and pharmacotherapy
- State the relationship between gut health, microbiome and diabetes and inflammation
- Describe 3 strategies to get our microbiome back to better health.
Can’t make it live? No worries. We will send post the recorded version to the Online University within 24 hours of the broadcast
Instructor: Beverly Thomassian RN, MPH, CDCES, has been Board Certified in Advanced Diabetes Management for over 20 years. She is an Associate Clinical Professor at UCSF, a working educator, and a nationally recognized diabetes expert. She has a Master’s Degree in Public Health from UCLA, with a focus on behavioral health and education.
All hours earned count toward your CDCES Accreditation Information
Sign up for Diabetes Blog Bytes – we post one daily Blog Byte from Monday to Friday. And of course, Tuesday is our Question of the Week. It’s Informative and FREE! Sign up below!
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the diabetes certification exams. CBDCE & ADCES does not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the certification exams, except for those published by CBDCE & ADCES.
Rationale of the Week | NPH Insulin 3 Times a Day?

For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on reviewing insulin dosing adjustments. 67% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question
Question: MR is 68 with type 2 diabetes and tells you that their provider increased their NPH insulin to three times a day and told them to adjust the NPH insulin dose based on their pre-meal blood sugar levels.
What is the best response?
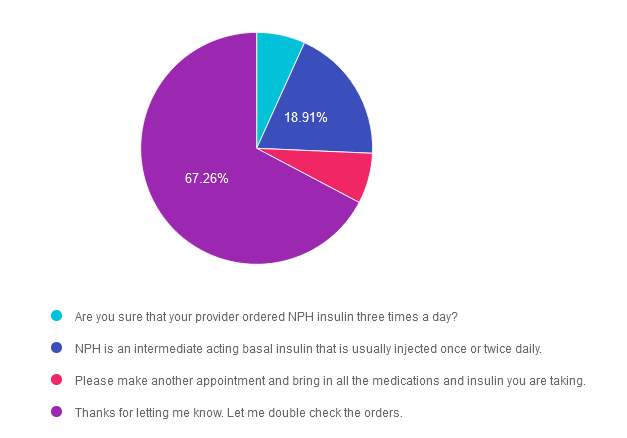
Answer Choices:
- Are you sure that your provider ordered NPH insulin three times a day?
- NPH is an intermediate acting basal insulin that is usually injected once or twice daily.
- Please make another appointment and bring in all the medications and insulin you are taking.
- Thanks for letting me know. Let me double check the orders.
Getting to the Best Answer
If you are thinking about taking the certification exam, this practice test question will set you up for success. Test writers anticipate possible answers based on the details in the question. They will wave those “juicy answers” right under your nose. Your job is to weed through the particulars, pluck out the most important elements and choose the BEST answer.
Answer 1 is incorrect. 6.77% chose this answer. “Are you sure that your provider ordered NPH insulin three times a day?” This is not the best response, since it might make the individual feel like they did something wrong and put them in a defensive position.
Answer 2 is incorrect. 18.91% of you chose this answer. “NPH is an intermediate acting basal insulin that is usually injected once or twice daily.” This is a correct factual answer, but it is not the best answer since it summarizes how NPH insulin works, but doesn’t address the root of the issue or assist with problem solving.
Answer 3 is incorrect. About 7.06% of respondents chose this. “Please make another appointment and bring in all the medications and insulin you are taking.” Although “brown bagging” meds is always a good idea, this answer means that MR would continue giving NPH three times a day on a sliding scale until the next appointment is available. This delay of action could result in unstable blood glucose levels.
Finally, Answer 4 is correct. 67.26% chose this answer. “Thanks for letting me know. Let me double check the orders.” This affirmational, person centered answer is the best choice! It acknowledges MR’s concern and is followed by action to help with problem solving. GREAT JOB!
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
Want to learn more about this question?
Level 4 | Basal Bolus Therapy in Hospitals
Now Recorded & Ready to Watch

Basal Bolus Therapy in Hospitals Topics:
- Discussing appropriate insulin dosing based on the individual’s clinical presentation.
- Apply dosing strategies to a variety of case studies.
- Introduce hard-to-manage situations that commonly occur in hospital settings.
- A discussion of solutions that will keep people living with diabetes safe & get glucose levels to goal.
- Sample basal/bolus & insulin drip guidelines plus lots of resource articles are included.
Can’t make it live? No worries. We will send post the recorded version to the Online University within 24 hours of the broadcast
Instructor: Beverly Thomassian RN, MPH, CDCES, has been Board Certified in Advanced Diabetes Management for over 20 years. She is an Associate Clinical Professor at UCSF, a working educator, and a nationally recognized diabetes expert. She has a Master’s Degree in Public Health from UCLA, with a focus on behavioral health and education.
All hours earned count toward your CDCES Accreditation Information
Sign up for Diabetes Blog Bytes – we post one daily Blog Byte from Monday to Friday. And of course, Tuesday is our Question of the Week. It’s Informative and FREE! Sign up below!
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the diabetes certification exams. CBDCE & ADCES does not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the certification exams, except for those published by CBDCE & ADCES.
Rationale of the Week | Why is annual kidney testing so important?

For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on the importance of annual kidney testing. 52% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question
Question: Only about 40% of individuals with diabetes get their kidney function tested annually.
Why is the evaluation of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and Urinary Albumin Creatinine Ratio (UACR) of critical importance for people with diabetes?
Answer Choices:
- Evaluate if peritoneal or hemodialysis is necessary for the individual.
- Determine best anti-hypertensive and glucose pharmacotherapy.
- Protect against immune mediated renal complications.
- Slow the progression of chronic kidney disease development.

Getting to the Best Answer
If you are thinking about taking the certification exam, this practice test question will set you up for success. Test writers anticipate possible answers based on the details in the question. They will wave those “juicy answers” right under your nose. Your job is to weed through the particulars, pluck out the most important elements and choose the BEST answer.
Answer 1 is incorrect. 3.43% chose this answer. “Evaluate if peritoneal or hemodialysis is necessary for the individual.” For people experiencing chronic kidney disease and worsening kidney function, they would need their GFR and UACR checked more frequently than annually along with a referral to a kidney specialist.
Answer 2 is correct. 51.56% of you chose this answer. “Determine best anti-hypertensive and glucose pharmacotherapy.” YES, this is the best answer. Knowing the GFR and UACR is critical to determining best medication therapies. For individuals with diabetes and a GFR less than 60 and/or a UACR of 30mg/g or greater, the ADA Standards recommend starting a SGLT-2 Inhibitor to preserve renal function. In addition, in individuals with hypertension and a UACR of 30mg/g or greater, the antihypertensive of choice is either an ACE or ARB. Yearly kidney function screening helps not only direct best diabetes and hypertensive medication therapy, it also identifies early kidney disease so preventive action can be taken.
Answer 3 is incorrect. About 8.48% of respondents chose this. “Protect against immune mediated renal complications.” This juicy answer is tempting and sounds good, but it is not an accurate response or a recognized condition.
Finally, Answer 4 is incorrect. 36.53% chose this answer. “Slow the progression of chronic kidney disease development.” This answer is tempting, but it does not address the intent of the question. Yearly kidney function testing informs the care providers about the health of the kidney. but simply testing does not slow kidney disease. Action is required.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
Want to learn more about this question?
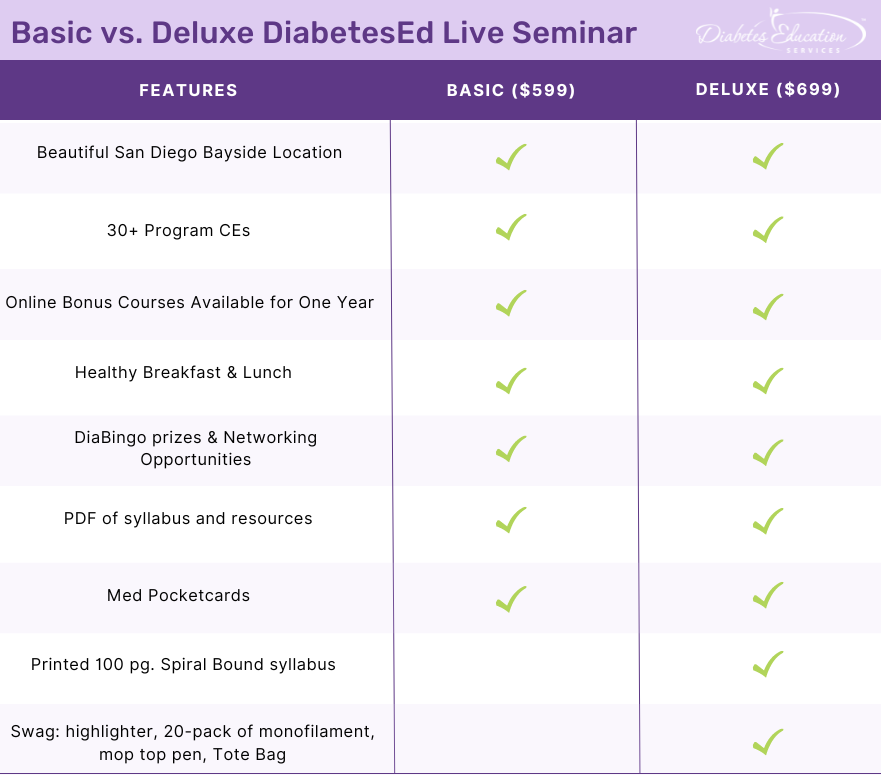
Join us LIVE in San Diego for our DiabetesEd Training Conference
October 11-13th, 2023

Two Registration Options
Join Coach Beverly and Team for two and a half days of knowledge-sharing, fun, networking, games with prizes, and “aha” moments in beautiful San Diego.
You don’t want to miss this one-of-a-kind learning opportunity. Get away from all those daily responsibilities and immerse yourself in a fun and intensive conference with plenty of networking opportunities.
Attendees will leave this conference with new tools and a more complete understanding of the latest advances in diabetes care, from medications to technology to Medical Nutrition Therapy!
Bring your colleagues and enjoy our friend discount.
Our team expertly translates the complex science of diabetes into understandable terms while keeping it real, practical, and fun.
Team of expert faculty includes:
- Diana Isaacs, PharmD, BCPS, BC-ADM, BCACP, CDCES – Educator of the Year, 2020
- Coach Beverly Thomassian, RN, MPH, CDCES, BC-ADM
- Ashley LaBrier, MS, RD, CDCES, Diabetes Program Coordinator
All hours earned count toward your CDCES Accreditation Information
Sign up for Diabetes Blog Bytes – we post one daily Blog Byte from Monday to Friday. And of course, Tuesday is our Question of the Week. It’s Informative and FREE! Sign up below!
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the CDCES exam. CBDCE does not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the CDCES exam, except for those published by CBDCE.
Rationale of the Week | C’est la vie with Different Time Zones & Diabetes

For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on living with diabetes & traveling to different timezones. 65% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question
Question: BT is heading to the south of France for a 25th wedding anniversary vacation. They usually take 32 units of glargine at 10 PM each night along with 5-7 units of bolus insulin with meals. There is a nine hour time difference between the United States and France.
They ask you how to adjust their basal insulin. What is the best response?
Answer Choices:
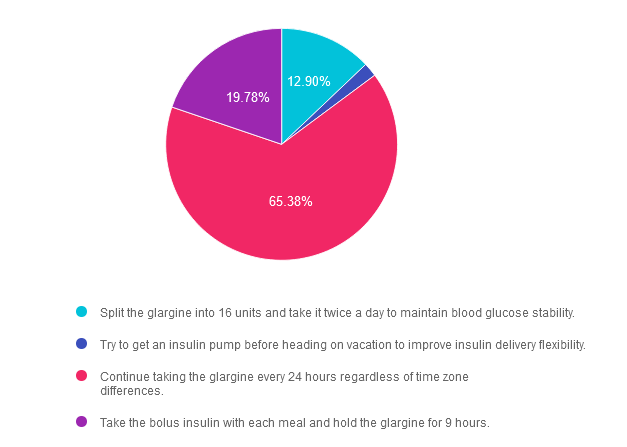
- Split the glargine into 16 units and take it twice a day to maintain blood glucose stability.
- Try to get an insulin pump before heading on vacation to improve insulin delivery flexibility.
- Continue taking the glargine every 24 hours regardless of time zone differences.
- Take the bolus insulin with each meal and hold the glargine for 9 hours.
Getting to the Best Answer
If you are thinking about taking the certification exam, this practice test question will set you up for success. Test writers anticipate possible answers based on the details in the question. They will wave those “juicy answers” right under your nose. Your job is to weed through the particulars, pluck out the most important elements and choose the BEST answer.
Answer 1 is incorrect. 12.90% chose this answer. “Split the glargine into 16 units and take it twice a day to maintain blood glucose stability.” Although a tempting answer, this action does not address or solve the issue of determining insulin injection timing in a different time zone.
Answer 2 is incorrect. 1.94% of you chose this answer. “Try to get an insulin pump before heading on vacation to improve insulin delivery flexibility.” This approach offers too big of an intervention based on BT’s question of when to dose their insulin in a different time zone.
Answer 3 is correct. About 65.38% of respondents chose this. “Continue taking the glargine every 24 hours regardless of time zone differences.” YES, GREAT JOB. Sometimes the most direct and simplest answer is the best answer. While traveling across time zones, as long as BT takes the basal insulin about every 24 hours and the bolus insulin with meals, they will be able to maintain their usual approach. However, accurate carb counting for French pastries and three course meals is a whole different challenge. : -)
Finally, Answer 4 is incorrect. 19.78% chose this answer. “Take the bolus insulin with each meal and hold the glargine for 9 hours.” The first part of this answer is correct, but the second part isn’t really accurate and it is too vague and confusing to make this answer the best choice. This is a great example of a “juicy answer”.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
Want to learn more about this practice question?
Join us LIVE in San Diego for our DiabetesEd Training Conference
October 11-13th, 2023

Two Registration Options

Join Coach Beverly and Team for two and a half days of knowledge-sharing, fun, networking, games with prizes, and “aha” moments in beautiful San Diego.
You don’t want to miss this one-of-a-kind learning opportunity. Get away from all those daily responsibilities and immerse yourself in a fun and intensive conference with plenty of networking opportunities.
Attendees will leave this conference with new tools and a more complete understanding of the latest advances in diabetes care, from medications to technology to Medical Nutrition Therapy!
Bring your colleagues and enjoy our friend discount.
Our team expertly translates the complex science of diabetes into understandable terms while keeping it real, practical, and fun.
Team of expert faculty includes:
- Diana Isaacs, PharmD, BCPS, BC-ADM, BCACP, CDCES – Educator of the Year, 2020
- Coach Beverly Thomassian, RN, MPH, CDCES, BC-ADM
- Ashley LaBrier, MS, RD, CDCES, Diabetes Program Coordinator
All hours earned count toward your CDCES Accreditation Information
Sign up for Diabetes Blog Bytes – we post one daily Blog Byte from Monday to Friday. And of course, Tuesday is our Question of the Week. It’s Informative and FREE! Sign up below!
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the diabetes certification exams. CBDCE & ADCES does not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the certification exams, except for those published by CBDCE & ADCES.
Rationale of the Week | What is best action for stage 2, type 1 diabetes?

For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on actions for managing stage 2, type 1 diabetes. 63% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question
Question: LT has just been diagnosed with stage 2, type 1 diabetes. They have 2 positive antibodies and their blood sugars are slightly elevated. They ask you if they are a candidate for “that therapy” that can protect their beta cells and slow progression of type 1 diabetes.
What is the most accurate response?
Answer Choices:
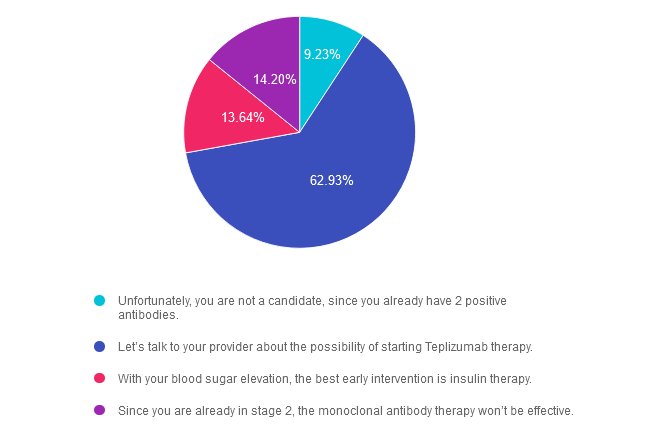
- Unfortunately, you are not a candidate, since you already have 2 positive antibodies.
- Let’s talk to your provider about the possibility of starting Teplizumab therapy.
- With your blood sugar elevation, the best early intervention is insulin therapy.
- Since you are already in stage 2, the monoclonal antibody therapy won’t be effective.
Getting to the Best Answer
If you are thinking about taking the certification exam, this practice test question will set you up for success. Test writers anticipate possible answers based on the details in the question. They will wave those “juicy answers” right under your nose. Your job is to weed through the particulars, pluck out the most important elements and choose the BEST answer.
Answer 1 is incorrect. 9.23% chose this answer. “Unfortunately, you are not a candidate, since you already have 2 positive antibodies.” Teplizumab IS indicated for the individual in stage 2 type 1 diabetes, or for those with two or more islet autoantibodies and abnormal glycemia but still asymptomatic. People with stage 2 type 1 diabetes, have a nearly 100% lifetime risk of progression to clinical (stage 3) type 1 diabetes and a 75% risk of developing the condition within 5 years.
Answer 2 is correct. 62.93% of you chose this answer. “Let’s talk to your provider about the possibility of starting Teplizumab therapy.” YES, this is the BEST ANSWER, According to ADA Standards, Teplizumab is the first disease-modifying therapy that impedes the progression of type 1 diabetes by binding to the surface of T cells to dampen the unwanted immune system response. It can delay the onset of symptomatic stage 3 type 1 diabetes in adults and children 8 years and older with stage 2 type 1 diabetes (see staging chart). It is administered by intravenous infusion once daily for 14 consecutive days and is expected to cost in the region of $200,000 for the course of treatment. Based on current data, it can delay the expression of stage 3 diabetes by 2 years or longer.
Answer 3 is incorrect. About 13.64% of respondents chose this. “With your blood sugar elevation, the best early intervention is insulin therapy.” Actually, according to ADA Guidelines, LT is a perfect candidate, since Teplizumab IS indicated for the individual in stage 2 type 1 diabetes, or for those with two or more islet autoantibodies and abnormal glycemia but still asymptomatic.
Finally, Answer 4 is incorrect. 14.20% chose this answer. “Since you are already in stage 2, the monoclonal antibody therapy won’t be effective.” Actually, according to ADA Guidelines, LT is a perfect candidate, since Teplizumab IS indicated for the individual in stage 2 type 1 diabetes, or for those with two or more islet autoantibodies and abnormal glycemia but still asymptomatic.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
For more information, see our blog on Teplizumab Therapy to Delay Type 1 Diabetes.
Want to learn more about this practice question?
Join us LIVE in San Diego for our DiabetesEd Training Conference
October 11-13th, 2023

Two Registration Options

Join Coach Beverly and Team for two and a half days of knowledge-sharing, fun, networking, games with prizes, and “aha” moments in beautiful San Diego.
You don’t want to miss this one-of-a-kind learning opportunity. Get away from all those daily responsibilities and immerse yourself in a fun and intensive conference with plenty of networking opportunities.
Attendees will leave this conference with new tools and a more complete understanding of the latest advances in diabetes care, from medications to technology to Medical Nutrition Therapy!
Bring your colleagues and enjoy our friend discount.
Our team expertly translates the complex science of diabetes into understandable terms while keeping it real, practical, and fun.
Team of expert faculty includes:
- Diana Isaacs, PharmD, BCPS, BC-ADM, BCACP, CDCES – Educator of the Year, 2020
- Coach Beverly Thomassian, RN, MPH, CDCES, BC-ADM
- Ashley LaBrier, MS, RD, CDCES, Diabetes Program Coordinator
All hours earned count toward your CDCES Accreditation Information
Sign up for Diabetes Blog Bytes – we post one daily Blog Byte from Monday to Friday. And of course, Tuesday is our Question of the Week. It’s Informative and FREE! Sign up below!
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the diabetes certification exams. CBDCE & ADCES does not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the certification exams, except for those published by CBDCE & ADCES.
Rationale of the Week | What explains nocturnal hyperglycemia?

For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on the effects of nocturnal hyperglycemia. 63% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question
Question: JR is 11 years old with type 1 diabetes and their parent shares their concern that the blood glucose seems to be rising overnight with morning hyperglycemia. The parent is worried that JR may be sneaking snacks in the night.
As a diabetes specialist, you know that this glucose rise is most likely due to:
Answer Choices:
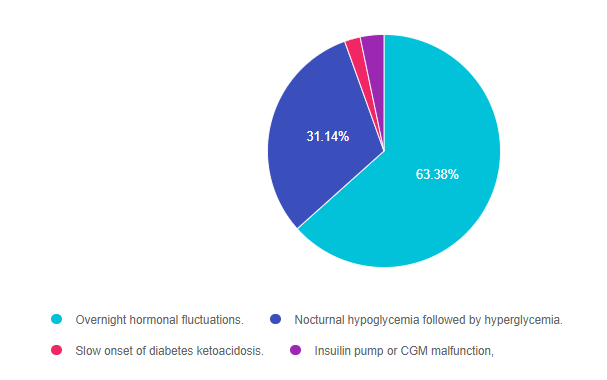
- Overnight hormonal fluctuations.
- Nocturnal hypoglycemia followed by hyperglycemia.
- Slow onset of diabetes ketoacidosis.
- Insulin pump or CGM malfunction.
Getting to the Best Answer
If you are thinking about taking the certification exam, this practice test question will set you up for success. Test writers anticipate possible answers based on the details in the question. They will wave those “juicy answers” right under your nose. Your job is to weed through the particulars, pluck out the most important elements and choose the BEST answer.
Answer 1 is correct. 63.38% chose this answer. “Overnight hormonal fluctuations.” YES, this is the best answer. There is an increased release of counterregulatory and growth hormones during the night, that is especially noteworthy during the teen years. These hormones contribute to insulin resistance and can cause morning hyperglycemia, often referred to as the Dawn Phenomena. For this reason, basal insulin dosing and rates need ongoing adjustment to address this nocturnal insulin resistance.
Answer 2 is incorrect. 31.14% of you chose this answer. “Nocturnal hypoglycemia followed by hyperglycemia.” Even though this phenomena, referred to as Somogyi effect, could cause morning hyperglycemia, there is no information in the test question that indicates JR is experiencing lows over night. Symptoms of hypoglycemia during the night might include; morning headaches, night sweats, vivid dreams or waking up hungry.
Answer 3 is incorrect. About 2.19% of respondents chose this. “Slow onset of diabetes ketoacidosis.” Even though hyperglycemia is associated ketoacidosis, JR has no symptoms of ketoacidosis like lethargy, fruity breath, urine ketones or dehydration.
Finally, Answer 4 is incorrect. 3.29% chose this answer. “Insulin pump or CGM malfunction.” While pump malfunction can lead to hyperglycemia, there is no information contained in the test question that would lead us to believe that JR is using any diabetes technology.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
Want to learn more about this practice question?
Join us LIVE in San Diego for our DiabetesEd Training Conference
October 11-13th, 2023

Two Registration Options

Join Coach Beverly and Team for two and a half days of knowledge-sharing, fun, networking, games with prizes, and “aha” moments in beautiful San Diego.
You don’t want to miss this one-of-a-kind learning opportunity. Get away from all those daily responsibilities and immerse yourself in a fun and intensive conference with plenty of networking opportunities.
Attendees will leave this conference with new tools and a more complete understanding of the latest advances in diabetes care, from medications to technology to Medical Nutrition Therapy!
Bring your colleagues and enjoy our friend discount.
Our team expertly translates the complex science of diabetes into understandable terms while keeping it real, practical, and fun.
Team of expert faculty includes:
- Diana Isaacs, PharmD, BCPS, BC-ADM, BCACP, CDCES – Educator of the Year, 2020
- Coach Beverly Thomassian, RN, MPH, CDCES, BC-ADM
- Ashley LaBrier, MS, RD, CDCES, Diabetes Program Coordinator
All hours earned count toward your CDCES Accreditation Information
Sign up for Diabetes Blog Bytes – we post one daily Blog Byte from Monday to Friday. And of course, Tuesday is our Question of the Week. It’s Informative and FREE! Sign up below!
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the CDCES exam. CBDCE does not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the CDCES exam, except for those published by CBDCE.
Rationale of the Week | Strategies to get glucose “under control”

For last week’s practice question, we review strategies for keeping glucose “under control.” 79% of respondents chose the best answer which is awesome. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question
Question: JR is 13 years old and has type 1 diabetes and their time in range is usually less than 50%. JR’s mom finds empty soda bottles hidden in the back of JR’s drawer along with some candy bars.
JR’s mom is very upset about this discovery and asks you how to get this “situation under control”. What is the most appropriate response?
Answer Choices:
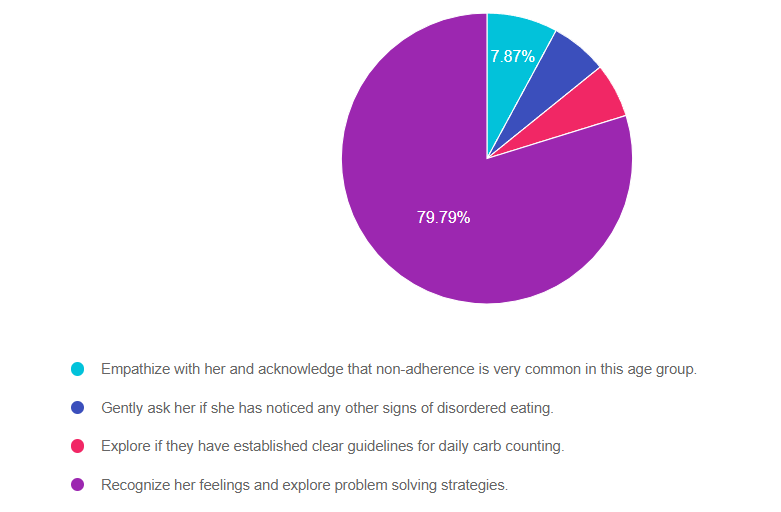
- Empathize with her and acknowledge that non-adherence is very common in this age group.
- Gently ask her if she has noticed any other signs of disordered eating.
- Explore if they have established clear guidelines for daily carb counting.
- Recognize her feelings and explore problem solving strategies.
Getting to the Best Answer
If you are thinking about taking the certification exam, this practice test question will set you up for success. Test writers anticipate possible answers based on the details in the question. They will wave those “juicy answers” right under your nose. Your job is to weed through the particulars, pluck out the most important elements and choose the BEST answer.
Answer 1 is incorrect. 7.87% chose this answer. “Empathize with her and acknowledge that non-adherence is very common in this age group.” Although this answer starts out with empathy, the second half reinforces the outdated concept of “non-adherence”. If JR is eating candy bars and drinking sodas, then hiding the evidence, indicates that JR might be experiencing big emotions around food restrictions that need exploration.
Answer 2 is incorrect. 6.30% of you chose this answer. “Gently ask her if she has noticed any other signs of disordered eating.” We can’t assume that JR has disordered eating because they are eating candy bars and drinking sodas, then hiding the evidence. This behavior may indicate that JR is experiencing big emotions around food restrictions that need exploration.
Answer 3 is incorrect. About 6.04% of respondents chose this. “Explore if they have established clear guidelines for daily carb counting.” Even though JR is eating candy bars and drinking sodas, then hiding the evidence, it doesn’t indicate that they additional information on carb counting or are in need of stricter guidelines.
Finally, Answer 4 is correct. 79.79% chose this answer. “Recognize her feelings and explore problem-solving strategies.” YES, GREAT JOB. This is the best answer. If JR is eating candy bars and drinking sodas, then hiding the evidence, this indicates that JR might be experiencing big emotions around food restrictions that need exploration.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
Want to learn more about this practice question?
Join us LIVE in San Diego for our DiabetesEd Training Conference
October 11-13th, 2023

Two Registration Options

Join Coach Beverly and Team for two and a half days of knowledge-sharing, fun, networking, games with prizes, and “aha” moments in beautiful San Diego.
You don’t want to miss this one-of-a-kind learning opportunity. Get away from all those daily responsibilities and immerse yourself in a fun and intensive conference with plenty of networking opportunities.
Attendees will leave this conference with new tools and a more complete understanding of the latest advances in diabetes care, from medications to technology to Medical Nutrition Therapy!
Bring your colleagues and enjoy our friend discount.
Our team expertly translates the complex science of diabetes into understandable terms while keeping it real, practical, and fun.
Team of expert faculty includes:
- Diana Isaacs, PharmD, BCPS, BC-ADM, BCACP, CDCES – Educator of the Year, 2020
- Coach Beverly Thomassian, RN, MPH, CDCES, BC-ADM
- Ashley LaBrier, MS, RD, CDCES, Diabetes Program Coordinator
All hours earned count toward your CDCES Accreditation Information
Sign up for Diabetes Blog Bytes – we post one daily Blog Byte from Monday to Friday. And of course, Tuesday is our Question of the Week. It’s Informative and FREE! Sign up below!
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the CDCES exam. CBDCE does not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the CDCES exam, except for those published by CBDCE.