Ready to get certified?
Free CDCES Coach App

Subscribe
eNewsletter
Download
Free Med Pocket Cards
Rationale of the Week | What Do New ADA Standards Say About Development of Type 2?
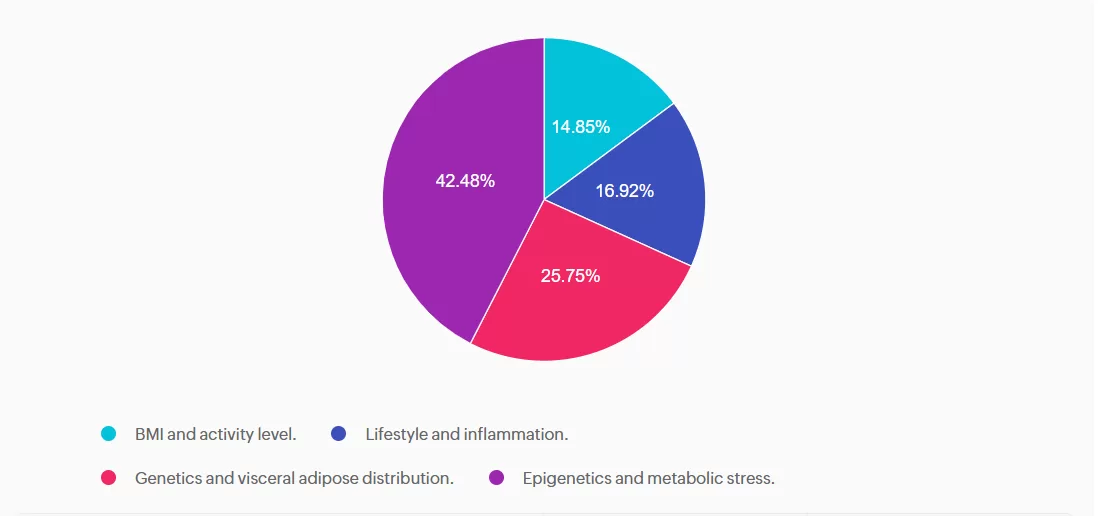
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on the new ADA Standards and the development of type 2 diabetes. 42.48% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

According to the new 2026 ADA Standards, “type 2 diabetes is associated with insulin secretory defects related to” which of the following?
- BMI and activity level.
- Lifestyle and inflammation.
- Genetics and visceral adipose distribution.
- Epigenetics and metabolic stress.
Getting to the Best Answer
Answer A is incorrect: 14.85% chose this answer, “BMI and activity level.” This answer is incorrect but tempting. BMI level is used as a a screening tool for prediabetes and diabetes risk, but is not included as a factor contributing to secretory defects. According to the ADA, there are four factors related to insulin secretory defects in type 2 diabetes. They include; genetics, epigenetics, metabolic stress and inflammation.
Answer B is incorrect: 16.92% chose this answer, “Lifestyle and inflammation.” This juicy answer is incorrect. Lifestyle is not a direct factor related to insulin secretory defects, but inflammation is a contributor. According to the ADA, there are four factors related to insulin secretory defects in type 2 diabetes. They include; genetics, epigenetics, metabolic stress and inflammation.
Answer C is incorrect: 25.75% chose this answer, “Genetics and visceral adipose distribution.” This answer is incorrect. Visceral adiposity is associated with an increased risk for diabetes, but does not contribute to insulin secretory defects. According to the ADA, there are four factors related to insulin secretory defects in type 2 diabetes. They include; genetics, epigenetics, metabolic stress and inflammation.
Answer D is correct: 42.48% chose this answer, “Epigenetics and metabolic stress.” This answer is correct, GREAT JOB! According to the ADA, there are four factors related to insulin secretory defects in type 2 diabetes. They include; genetics, epigenetics, metabolic stress and inflammation.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
Join Coach Bev!
Take a Deep Dive Into the 2026 ADA Standards
On January 29th, 2026 at 11:30 AM PST

Rationale of the Week | Individual vs. Group DSMES
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on which of the following would NOT justify providing individual DSMES instead of group DSMES. % of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

After the initial assessment JM is scheduled for an individual visit instead of a group DSMES class.
According to Medicare guidelines, which of the following would NOT justify providing individual DSMES instead of group DSMES?
- When scheduling, JM requested an individual appointment
- The referral for DSMES stated JM has a language barrier
- A group DSMES class is not available within the next 3 months
- JM was referred for training on starting insulin therapy
Getting to the Best Answer
Answer A is correct: % chose this answer, “When scheduling, JM requested an individual appointment” Answer A is correct; it does NOT justify individual DSMES. Although diabetes care should be patient-centered, patient preference alone does not meet Medicare criteria for individual DSMES. Medicare requires the referring provider document justification of
barriers to group learning which can include clinical, educational, or psychosocial need.
Answer B is incorrect: % chose this answer, “The referral for DSMES stated JM has a language barrier” Answer B is incorrect and does justify individual DSMES. Language barriers can significantly limit participation in group DSMES. Medicare recognizes a referral with stated language and communication needs as valid justification for an individual visit.
Answer C is incorrect: % chose this answer, “A group DSMES class is not available within the next 3 months” Answer C is incorrect and does justify individual DSMES. Medicare will approve individual DSMES if no group class is available for two months or longer from the date on the referral.
Answer D is incorrect: % chose this answer, “JM was referred for training on starting insulin therapy” Answer D is incorrect and does justify individual DSMES. A referral for initiation of insulin therapy requires individualized instruction. This can include injection technique, dose adjustment, hypoglycemia prevention, and problem-solving. Medicare considers this
an appropriate reason for individual DSMES.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
Learn More With Our Online Boot Camps & Conferences
Prepare for the CDCES Exam

Course credits through AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™, ACPE, ANCC, and CDR!
Get exam-ready with confidence.
Our CDCES Boot Camp Online Prep Bundle is a comprehensive, high-impact program built specifically for healthcare professionals preparing for the Certified Diabetes Care and Education Specialist (CDCES) exam who want to level-up their clinical knowledge and skills.
✔ Learn at your pace with expert-led, exam-focused content
✔ Everything you need—organized, practical, and in one place
✔ Perfect for self-directed learners who want complete, person-centered content for clinical practice and exam prep.
✔ Build knowledge, sharpen test-taking skills, and prepare with confidence—on your schedule.
Focused. Flexible. Proven.
Basic & e-Deluxe CDCES Boot Camp Bundle Includes:
- Levels 1, 2, and 3 of our Online University
- 30+ expert-led courses
- 50 CE/CPEUs
- 400+ online practice questions
- Handouts, podcast, video and one year access—all in one streamlined platform.
Prepare for the BC-ADM Exam

Course credits through AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™, ACPE, ANCC, and CDR!
Get exam-ready with confidence.
Our comprehensive BC-ADM Online Study Programs are specifically designed for healthcare professionals who are studying for the Board Certified in Advanced Diabetes Management (BC-ADM) exam.
✔ Learn at your pace with expert-led, exam-focused content
✔ Everything you need—organized, practical, and in one place
✔ Perfect for self-directed learners who want complete, person-centered content for clinical practice and exam prep.
✔ Build knowledge, sharpen test-taking skills, and prepare with confidence—on your schedule.
Focused. Flexible. Proven.
Basic & e-Deluxe BC-ADM Boot Camp Bundle include:
- Levels 2, 3, and 4 of our Online University
- 30+ expert-led courses
- 50 CE/CPEUs
- 400+ online practice questions
- Handouts, podcast, video and one year access—all in one streamlined platform.
Virtual DiabetesEd Training Conference
April 15th-17th, 2026
Gain fresh insights, practical tools, and a deeper understanding of the latest in person-centered diabetes care. Our expert team brings the ADA Standards of Care to life—covering medications, behavior change, technology, and more!
Registration Options at a Glance
- 📜 Essentials: Includes registration and electronic syllabus.
- 🌟 Deluxe: Includes registration, electronic syllabus, and the ADA Standards Book for deeper study.
- 🏆 Complete: Best value! Includes everything listed above, plus the ADCES Review Guide of over 400 practice questions for exam prep.
Registration Fee includes
- 🎤 3 days of engaging, expert-led education
- 📘 100-page electronic syllabus +
- 🎓 12 FREE bonus online courses ($375 value) to boost your prep
Rationale of the Week | Indications for DXA Assessment of Bone Mineral Density
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on what individuals should be recommended to have a bone density evaluation using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry to evaluate for bone loss, according to the 2026 ADA Standards of Care. % of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

According to the 2026 ADA Standards of Care, what individuals should be recommended to have a bone density evaluation using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry to evaluate for bone loss?
- A 67-year-old female living with frequent falls and no bone fractures. She is newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, taking only metformin, with a bone density test 1 year ago that was normal.
- A 49-year-old premenopausal woman with prediabetes who has a low vitamin D level but no history of bone fracture.
- A 59-year-old male living with type 2 diabetes, taking pioglitazone, and whose A1c is 8.7%.
- A 43-year-old man living with type 2 diabetes for five years, taking metformin and an SGLT2 inhibitor, without diabetes related complications, but did break his arm as a child.
Getting to the Best Answer
Answer A is incorrect: % chose this answer, “A 67-year-old female living with frequent falls and no bone fractures. She is newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, taking only metformin, with a bone density test 1 year ago that was normal.” This answer is incorrect. Per the 2026 ADA Standards of Care, she does meet criteria for assessing bone health due to her diagnosis of type 2 diabetes and risk factor of frequent falls, but she had a bone density test 1 year ago. Currently, the recommendation is to re-evaluate the bone density test in 2-3 years.
Answer B is incorrect: % chose this answer, “A 49-year-old premenopausal woman with prediabetes who has a low vitamin D level but no history of bone fracture.” This answer is incorrect. Per the 2026 ADA Standards of Care, it is recommended to assess bone health in postmenopausal women with other diabetes specific risk factors. This risk factor does not include low vitamin D levels.
Answer C is correct: % chose this answer, “A 59-year-old male living with type 2 diabetes, taking pioglitazone, and whose A1c is 8.7%.” This answer is correct. Per the 2026 ADA Standards of Care, bone health should be assessed in men aged ≥50 years with type 2 diabetes and an A1c >8%. He is also on pioglitazone, a thiazolidinedione, which is another risk factor for low bone density.
Answer D is incorrect: % chose this answer, “A 43-year-old man living with type 2 diabetes for five years, taking metformin and an SGLT2 inhibitor, without diabetes related complications, but did break his arm as a child.” This answer is incorrect. Per the 2026 ADA Standards of Care, he has no diabetes-specific risk factors for bone loss. Diabetes duration is less than 10 years, he has no diabetes related complications such as peripheral or autonomic neuropathies, he is not on a high-risk medication for bone loss, and he has not had a bone fracture as an adult.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
Learn More With Our Online Boot Camps & Conferences
Prepare for the CDCES Exam

Course credits through AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™, ACPE, ANCC, and CDR!
Get exam-ready with confidence.
Our CDCES Boot Camp Online Prep Bundle is a comprehensive, high-impact program built specifically for healthcare professionals preparing for the Certified Diabetes Care and Education Specialist (CDCES) exam who want to level up their clinical knowledge and skills.
CDCES Bundle: What’s Included?
- 30+ expert-led courses from the fundamentals to the ADA standards, to test strategies and exam mastery! Includes Levels 1, 2 and 3.
- 50+ CE credits (AMA PRA Category 1™, ACPE, ANCC, CDR accredited)
- 400+ practice questions to test your knowledge and build confidence
- Multiple learning formats: video presentations, audio podcasts, and downloadable handouts
- 1 full year of on-demand access to study at your own pace
Choose Your Bundle:
✔ Basic CDCES Boot Camp – From the fundamentals, to the ADA standards, to test strategies and exam mastery! This complete exam prep includes Levels 1, 2, and 3 (30+ courses, 50+ CEs, 400+ practice questions)
✔ e-Deluxe CDCES Boot Camp – Everything in Basic PLUS the [e-Book] ADCES Certification Review Guide | 6th Edition (475+ practice questions)
✔ Mini CDCES Boot Camp – Accelerated program for experienced healthcare professionals (skips Level 1 | Diabetes Fundamentals, includes Levels 2 & 3, 20+ courses, 40+ CEs, 325+ practice questions).
Prepare for the BC-ADM Exam

Course credits through AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™, ACPE, ANCC, and CDR!
Get exam-ready with confidence.
Our comprehensive BC-ADM Online Study Programs are specifically designed for advanced level healthcare professionals who are studying for the Board Certified in Advanced Diabetes Management (BC-ADM) exam.
BC-ADM Bundle: What’s Included?
- 30+ expert-led courses covering advanced diabetes management, ADA standards, medication review, insulin calculations and tech topics!
- 50+ CE credits (AMA PRA Category 1™, ACPE, ANCC, CDR accredited). Includes advanced levels 2, 3 and 4.
- 400+ practice questions to test your knowledge and build BC-ADM test confidence.
- Multiple learning formats: video presentations, audio podcasts, and downloadable handouts
- 1 full year of on-demand access to study at your own pace
Choose Your Bundle:
✔ Basic BC-ADM Boot Camp – Complete exam prep includes Levels 2, 3, and 4 (30+ courses, 50+ CEs, 400+ practice questions)
✔ e-Deluxe BC-ADM Boot Camp – Everything in Basic PLUS the ADCES Certification Review Guide E-book with an additional 475+ practice questions.
Virtual DiabetesEd Training Conference
April 15th-17th, 2026
Gain fresh insights, practical tools, and a deeper understanding of the latest in person-centered diabetes care. Our expert team brings the ADA Standards of Care to life—covering medications, behavior change, technology, and more!
Registration Options at a Glance
- 📜 Essentials: Includes registration and electronic syllabus.
- 🌟 Deluxe: Includes registration, electronic syllabus, and the ADA Standards Book for deeper study.
- 🏆 Complete: Best value! Includes everything listed above, plus the ADCES Review Guide of over 400 practice questions for exam prep.
Registration Fee includes
- 🎤 3 days of engaging, expert-led education
- 📘 100-page electronic syllabus +
- 🎓 12 FREE bonus online courses ($375 value) to boost your prep
Rationale of the Week | What Year ADA Standards Should JR Study?
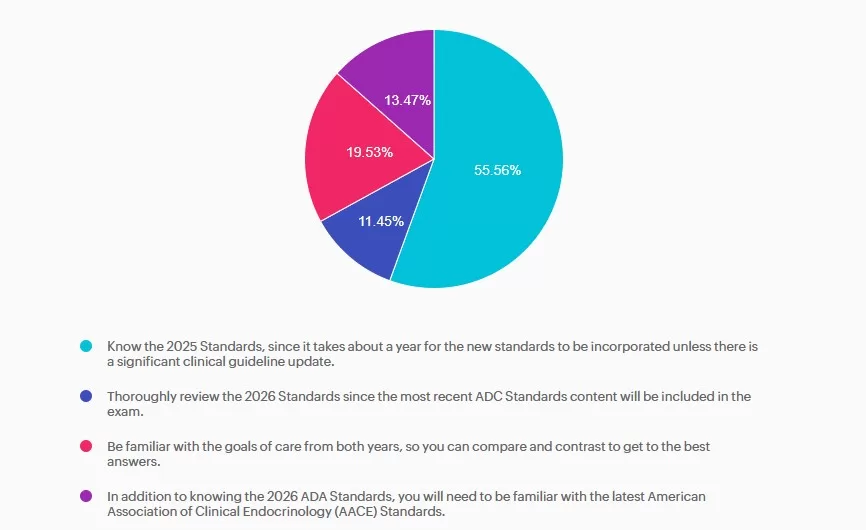
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on JR studying to take their CDCES exam, and they have questions studying for the 2025 or 2026 ADA Standards of Care. 55.56% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

JR has been diligently studying to take their CDCES exam at the end of January 2026. They are wondering if they should study the 2025 or 2026 ADA Standards of Care.
As a mentor to healthcare professionals entering the field of diabetes, what do you recommend?
- Know the 2025 Standards, since it takes about a year for the new standards to be incorporated unless there is a significant clinical guideline update.
- Thoroughly review the 2026 Standards since the most recent ADC Standards content will be included in the exam.
- Be familiar with the goals of care from both years, so you can compare and contrast to get to the best answers.
- In addition to knowing the 2026 ADA Standards, you will need to be familiar with the latest American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE) Standards.
Getting to the Best Answer
Answer A is correct: 55.56% chose this answer, “Know the 2025 Standards, since it takes about a year for the new standards to be incorporated unless there is a significant clinical guideline update.” Answer A is the BEST answer. It takes at least a year for the CBDCE to update the exam based on the ADA Standards. Knowing the 2025 Standards along with any urgent clinical updates announced in 2026 will help prepare JR for success.
Answer B is incorrect: 11.45% chose this answer, “Thoroughly review the 2026 Standards since the most recent ADC Standards content will be included in the exam.” Answer B is not the best answer. Since it takes at least a year for the CBDCE to update the exam based on the ADA Standards, JR can feel comfortable knowing the 2025 Standards along with any urgent clinical updates announced in 2026.
Answer C is incorrect: 19.53% chose this answer, “Be familiar with the goals of care from both years, so you can compare and contrast to get to the best answers.” Answer C is not the best answer. Thinking about comparing and contrasting two consecutive years standards and lead to testing confusion. JR can feel comfortable knowing the 2025 Standards along with any urgent clinical updates announced in 2026.
Answer D is incorrect: 13.47% chose this answer, “In addition to knowing the 2026 ADA Standards, you will need to be familiar with the latest American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE) Standards.” Answer D is not the best answer. Since it takes at least a year for the CBDCE to update the exam based on the ADA Standards, JR can feel comfortable knowing the 2025 Standards along with any urgent clinical updates announced in 2026.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
Get Ready For Your CDCES Exam With Our Upcoming Webinars!
Rationale of the Week | Storing insulin in work bag?
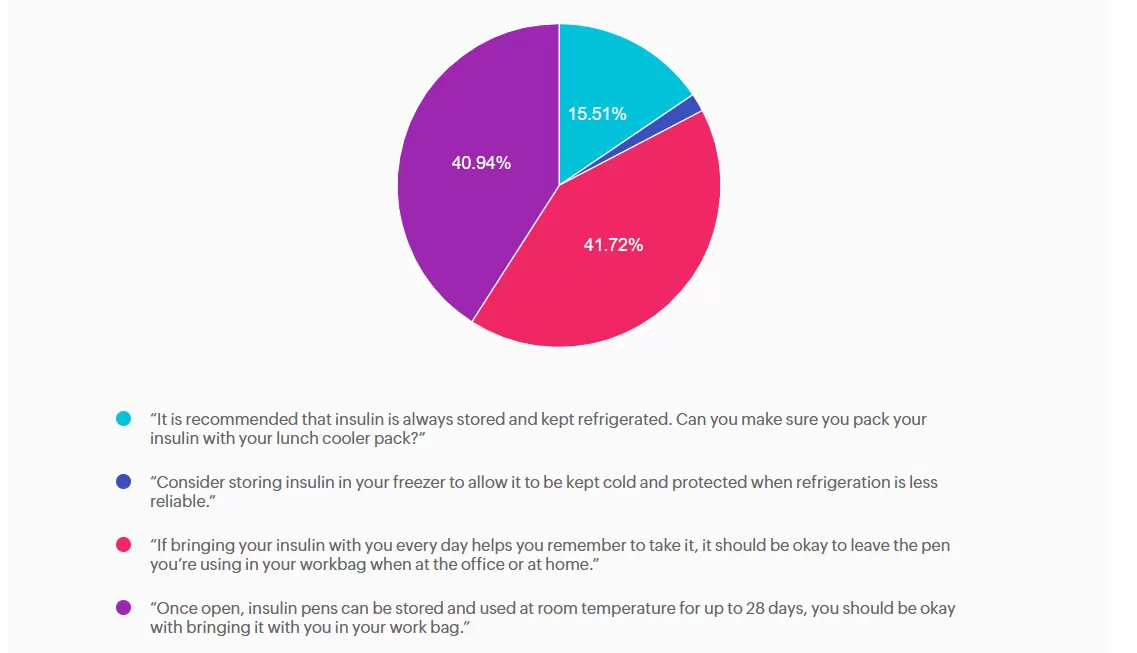
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on SJ having questions about their insulin pen, and what would be the best response. 41.72% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

SJ is 52 years old with a 10-year history of type 2 diabetes. They recently started on insulin degludec U-100 Flex Touch pen 15 units per day. At a follow-up visit, SJ brings their insulin pen and mentions they have been keeping it in their work bag since starting therapy. They are unsure how long they can continue to use this same pen.
What is the best advice for SJ for insulin storage in this situation?
- “It is recommended that insulin is always stored and kept refrigerated. Can you make sure you pack your insulin with your lunch cooler pack?”
- “Consider storing insulin in your freezer to allow it to be kept cold and protected when refrigeration is less reliable.”
- “If bringing your insulin with you every day helps you remember to take it, it should be okay to leave the pen you’re using in your workbag when at the office or at home.”
- “Once open, insulin pens can be stored and used at room temperature for up to 28 days, you should be okay with bringing it with you in your work bag.”
Getting to the Best Answer
Answer A is incorrect: 15.51% chose this answer, “It is recommended that insulin is always stored and kept refrigerated. Can you make
sure you pack your insulin with your lunch cooler pack?” While refrigeration is ideal for insulin storage, insulin does not always need to be refrigerated. Once in use, most insulins, including degludec, are stable at room temperature (below 86F or 30 C). Advising refrigeration may create unnecessary barriers and does not reflect degludec’s stability profile.
Answer B is incorrect: 1.83% chose this answer, “Consider storing insulin in your freezer to allow it to be kept cold and protected when
refrigeration is less reliable.” Freezing damages insulin molecules, making the insulin ineffective and unsafe to use. This option contradicts manufacturer and clinical safety guidance.
Answer C is correct: 41.72% chose this answer, “If bringing your insulin with you every day helps you remember to take it, it should be
okay to leave the pen you’re using in your workbag when at the office or at home.” Insulin degludec is stable at room temperature below 86°F (30°C) for up to 56 days (8 weeks) once opened. If SJ’s work bag is not exposed to excessive heat or freezing, keeping the pen there is acceptable and may in fact support consistent dosing. We can also calculate SJ’s monthly insulin pen usage (15 units per day + 2 unit prime per injection = 510 units per month or 2 pens per month), knowing he will easily use more insulin than open insulin pen stability time window.
Answer D is incorrect: 40.94% chose this answer, “Once open, insulin pens can be stored and used at room temperature for up to 28 days, you should be okay with bringing it with you in your work bag.” While it is correct that insulin does not always require refrigeration once in use, the specific duration varies by insulin type; degludec lasts longer than 28 days.
To learn more, check out our Insulin Storage Cheat Sheet.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
ADA Standards of Care Complete Review 2026
With Coach Beverly - Join us live on January 29th
Course Credits through AMA PRA Category 1 Credits, ACPE, ANCC and CDR

Rationale of the Week | Symptoms of Diabetes Type 3c
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on RT forgetting their insulin, and what would be the best response. 62.93% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

JR was recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, but based on their history of pancreatitis, you suspect JR actually has Diabetes Type 3c.
Which of the following symptoms match a diagnosis of Diabetes Type 3c?
- Fatty stools and insulin sensitivity.
- Frequent urination and insulin resistance.
- Neuropathy and unexplained weight gain.
- Family history of diabetes type 3c and polyphagia.

Getting to the Best Answer
Answer A is correct: 62.93% chose this answer, “Fatty stools and insulin sensitivity.” Steatorrhea, or fatty stools, results from poor fat digestion due to insufficient pancreatic enzymes—a key feature of type 3c diabetes, with it’s hallmark exocrine enzyme insufficiency. People with diabetes type 3c, can also be very insulin sensitive, since they don’t have the insulin resistance associated with type 2 diabetes. In addition to diabetes medications, they may benefit from pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT) to improve absorption of fatty foods and decrease steatorrhea.
Answer B is incorrect: 15.47% chose this answer, “Frequent urination and insulin resistance.” Frequent urination and insulin resistance is associated with type 2 diabetes. With type 3c, since many of the beta cells are destroyed due to trauma not genetics, these individuals may have polyuria from hyperglycemia, but they are not usually insulin resistant, just deficient.
Answer C is incorrect: 7.47% chose this answer, “Neuropathy and unexplained weight gain.” They may get neuropathy if their blood glucose is elevated for a long period of time, but that is not part of the differential. People with type 3c usually experience weight loss due to the lack of pancreatic enzymes that help with nutrient absorption.
Answer D is incorrect: 14.13% chose this answer, “Family history of diabetes type 3c and polyphagia.” Type 3c diabetes is not passed on through genes, it is due to exocrine damage to the pancreas which can lead to destruction of beta cells. Most common causes of diabetes type 3c include pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, pancreatic cancer, and hemochromatosis. Some people could experience extreme hunger if their glucose levels are elevated for an extended period of time.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
Learn more about Diabetes Type 3c in our “From the Gut to the Butt Webinar”
Recorded and Ready for Viewing.
Rationale of the Week | Gestational Diabetes: Diabetes Care in the Fourth Trimester
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on Gestational Diabetes: Diabetes Care in the Fourth Trimester. 51% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

MT is a 29-year-old with Type 1 diabetes who is currently 14 weeks pregnant. She uses a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) with concurrent fingersticks and uploads her glucose data weekly. Her CGM settings was already set to the recommended time in
range and the latest CGM report shows the following: time in range (TIR): 67%, time below range: 6%, time above range: 27%.
Based on current ADA Standard of Care, which of the following statements is most accurate regarding her CGM values?
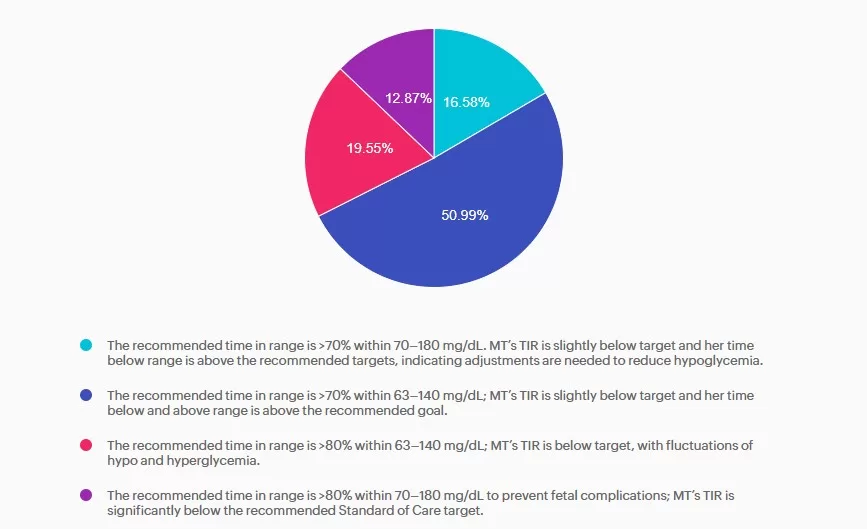
- The recommended time in range is >70% within 70–180 mg/dL. MT’s TIR is slightly below target and her time below range is above the recommended targets, indicating adjustments are needed to reduce hypoglycemia.
- The recommended time in range is >70% within 63–140 mg/dL; MT’s TIR is slightly below target and her time below and above range is above the recommended goal.
- The recommended time in range is >80% within 63–140 mg/dL; MT’s TIR is below target, with fluctuations of hypo and hyperglycemia.
- The recommended time in range is >80% within 70–180 mg/dL to prevent fetal complications; MT’s TIR is significantly below the recommended Standard of Care target.
Getting to the Best Answer
Answer A is incorrect: 16.58% chose this answer, “The recommended time in range is >70% within 70–180 mg/dL. MT’s TIR is slightly below target and her time below range is above the recommended targets, indicating adjustments are needed to reduce hypoglycemia.” Answer A is incorrect. The answer uses non-pregnancy CGM target range of 70–180 mg/dL. Pregnancy target range for individuals with type 1 diabetes are lower, keep reading for the best answer.
Answer B is correct: 51% chose this answer, “The recommended time in range is >70% within 63–140 mg/dL; MT’s TIR is slightly below target and her time below and above range is above the recommended goal.” Answer B is correct. Based on the 2025 ADA Standards of Care the recommended time in range targets for individuals with type 1 diabetes during pregnancy is >70% between 63-140 mg/dL, < 4% under 63 mg/dL with < 1 % under 54 mg/dL, and < 25% over 140 mg/dL.
Answer C is incorrect: 19.55% chose this answer, “The recommended time in range is >80% within 63–140 mg/dL; MT’s TIR is below target, with fluctuations of hypo and hyperglycemia.” Answer C is incorrect. The time in range target is above the evidenced-based
minimum and MT is having frequent hypoglycemia in addition to hyperglycemia, both outside the goal ranges.
Answer D is incorrect: 12.87% chose this answer, “The recommended time in range is >80% within 70–180 mg/dL to prevent fetal
complications; MT’s TIR is significantly below the recommended Standard of Care target.” Answer D is incorrect. The recommended target range for individuals with type 1diabetes during pregnancy is 63-140 mg/dL as stated above.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
Standards 1 – 16:
ADA Standards of Care Complete Review 2026 Update
with Coach Beverly Thomassian RN, MPH, CDCES, BC-ADM
Join us live on January 29th for the 2026 update!
Course credits through AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™, ACPE, ANCC, and CDR!
This course is included in our Level 2 | Standards of Care Intensive
This Level 2 course fulfills the annual ADA Standards of Care component required for CDCES certification renewal. They also count toward your CDCES and BC-ADM certification CE requirements.

Join Coach Bev for an in-depth exploration of the 2026 ADA Standards! This is our most popular course of the year, offering the perfect opportunity to immerse yourself in the essential content featured in this comprehensive 300-page clinical guidebook.
This course, updated annually, is an essential review for anyone in the field of diabetes. Join Coach Beverly as she summarizes the annual updates to the American Diabetes Association’s (ADA) Standard of Medical Care in Diabetes. This course provides critical teaching points and content for healthcare professionals involved in diabetes care and education.
Topics:
- State critical changes & updates to the annual ADA Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes.
- Identification of key diabetes care and clinical elements in the ADA Standards of Care.
- Discuss how diabetes health care professionals can apply this information in their clinical setting.
Course Objectives:
Upon completion of this activity, participants will be able to:
- Describe the application of the American Diabetes Association Standards of Care for people living with prediabetes and diabetes across the lifespan and in different care settings.
- List the different pharmacologic and lifestyle treatment options to manage hyperglycemia, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia and improve health outcomes for people living with diabetes.
- State the components of a physical assessment, management of hyperglycemic crises, identification of diabetes co-conditions, and treatment approaches to prevent complications and promote the best quality of life for people with diabetes.
- Discuss the steps involved in assessing and promoting well-being in individuals and populations while exploring psychosocial issues and considering social determinants of health.
Rationale of the Week | RT Forgot Their Insulin- Best Response?
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on RT forgetting their insulin, and what would be the best response. 63.10% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

RT has type two diabetes and has been maintaining a time and range of 70% or greater. However, when they show up at the office, the last week’s time in range dropped to 30%. You ask what was different this week from the previous few months. RT tells you they went on a five day fishing trip and forgot their insulin.
What’s the best response?
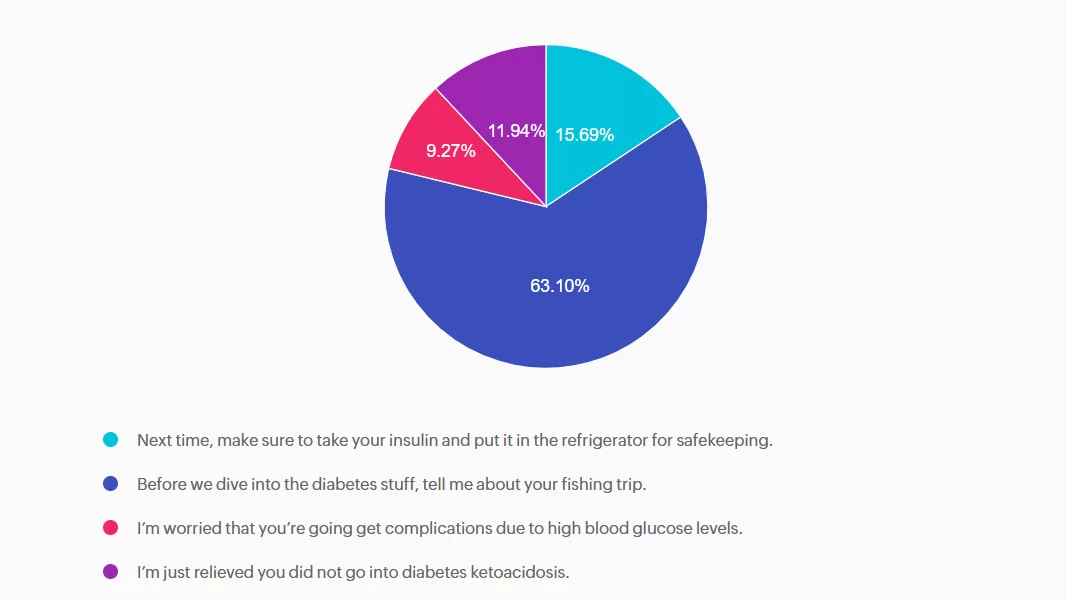
- Next time, make sure to take your insulin and put it in the refrigerator for safekeeping.
- Before we dive into the diabetes stuff, tell me about your fishing trip.
- I’m worried that you’re going get complications due to high blood glucose levels.
- I’m just relieved you did not go into diabetes ketoacidosis.
Getting to the Best Answer
Answer A is incorrect: 15.69% chose this answer, “Next time, make sure to take your insulin and put it in the refrigerator for safekeeping.” This approach goes under the compliance model, where the healthcare professional only provides one way instruction without considering the individuals insights and problem solving skills. We want to work toward a person-centered collaborative approach to foster connection.
Answer B is correct: 63.10% chose this answer, “Before we dive into the diabetes stuff, tell me about your fishing trip.” Great job! This is the best answer. By asking RT about their fishing trip first, you let them know you are interested in their life experiences and this helps to establish a connection. After hearing about the trip, we might pivot and say something like, “Do you want to discuss strategies to bring your insulin on your next fishing trip?”
Answer C is incorrect: 9.27% chose this answer, “I’m worried that you’re going get complications due to high blood glucose levels.” Although this statement shows concern, it is unlikely that RT will get diabetes complications from not taking their insulin for a few days. This statement could lead to feelings of shame and failure, and may close the door to making a meaningful connection.
Answer D is incorrect: 11.94% chose this answer, “I’m just relieved you did not go into diabetes ketoacidosis.” This statement could evoke feelings of guilt and shame, that could close the door to future communication. And if RT has type 2 diabetes, the chance of DKA is minimal. Instead of focusing on the HCP feelings, let’s check in with RT and explore problem solving strategies for future trips that would work for them.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!