
Subscribe
eNewsletter

Ready to get certified?
Free CDCES Coach App
Download
Free Med Pocket Cards

LS wears an insulin pump and uses lispro insulin. LS has an average basal rate of 0.6 units and hour, a 1:15 carb ratio and a 1:50 correction ratio. Based on the ambulatory glucose profile, LS is experiencing elevated glucose levels from 4am to 7am. To get glucose to target, what is the best next step?
Click Here to Test your Knowledge
Learn Test-Taking Secrets with Coach Bev – Option to add on 200+ Computerized Practice Test Questions for $49
During this webinar, Coach Beverly will help you transform your nervousness into focused energy that will help you succeed. She will provide test-taking tips based on her experience taking the certification exam six times.
To provide plenty of practice, Coach Beverly will sample 20 test questions that have been plucked from our Test Taking Toolkit during this live webinar.
She will explain how to dissect the question, eliminate wrong answers and avoid getting lured in by juicy answers.
Includes a review of 20 sample test questions with test taking strategies.
This includes access to the recorded version of this webinar on your Online University Student Portal.
Plus, the Test Taking Toolkit provides you with over 200+ sample online practice questions, simulating the exam experience.
A perfect way to assess your knowledge and create a focused study plan, while increasing your test-taking confidence.

Whether you are new to diabetes or a seasoned expert, you’ll benefit from this virtual conference with the latest research plus critical content that you can immediately apply to your clinical practice.
Download Course Flyer | Download Schedule
If you are seeking a state-of-the-art review of current diabetes care, this course is for you. Our team has been fine-tuning this course for over fifteen years, and we know what you need. This program can also be a great addition to your CDCES or BC-ADM exam study plan.
Join us LIVE for this Virtual Course and enjoy a sense of community!
Team of expert faculty includes:
Deluxe Option for $499: Virtual Program includes:
Deluxe Version includes Syllabus, Standards and Swag*:
Basic Option for $399: Virtual Program includes:
Don’t worry if you can’t make it live. Your registration guarantees access to the recorded version in the Online University.
All hours earned count toward your CDCES Accreditation Information
Sign up for Diabetes Blog Bytes – we post one daily Blog Byte from Monday to Friday. And of course, Tuesday is our Question of the Week. It’s Informative and FREE! Sign up below!
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the CDCES exam. CBDCE does not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the CDCES exam, except for those published by CBDCE.
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed test takers on fatty liver disease. 57% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question
Question: 45 to 75% of individuals with type 2 diabetes have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). NAFLD has associated with an increased risk of steatohepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Which of the following statements is true based on ADA Standards of Care?
Answer Choices:
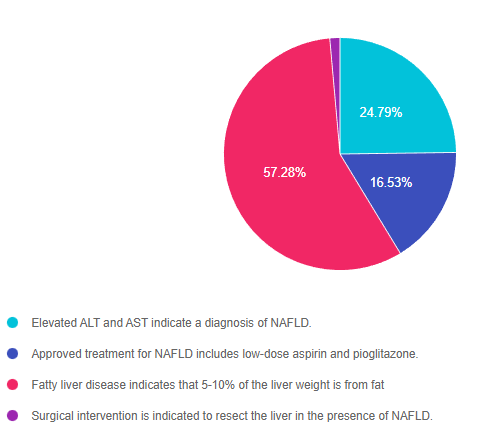
As shown above, the most common choice was option 3, the second most common answer was option 1, then option 2, and finally 4.
Answer 1 is incorrect. 24.79% chose this answer, “Elevated ALT and AST indicate a diagnosis of NAFLD.” These two liver enzyme tests certainly indicate liver inflammation and are a signal that further investigation is warranted. However, to confirm and diagnose NAFLD, a comprehensive review of patient history, lab results, liver imaging studies and possibly a biopsy are required.
Answer 2 is incorrect. 16.53% of you chose this answer, “Approved treatment for NAFLD includes low-dose aspirin and pioglitazone.” The cornerstones of treatment for NAFLD are nutrition therapy interventions with a focus on decreasing processed foods, sugary beverages and foods high in saturated fat. Plus, increasing intake of whole foods and committing to a structured physical activity plan to decrease visceral and hepatic adiposity is imperative. There is no officially approved medication to treat NAFLD, but pioglitazone and GLP-1 RA’s appear to decrease fatty liver based on current studies.
Answer 3 is correct. 57.28% of respondents chose this answer, “Fatty liver disease indicates that 5-10% of the liver weight is from fat.” GREAT JOB, this is the best answer. The good news is that weight loss and increased activity are very effective in treating fatty liver disease. A weight loss of 7-10% linked with a 50% drop in liver fat. Every pound lost makes a big difference. The cornerstones of treatment for NAFLD are nutrition therapy interventions with a focus on decreasing processed foods, sugary beverages and foods high in saturated fat. Plus, increasing intake of whole foods and committing to a structured physical activity plan to decrease visceral and hepatic adiposity is imperative.
Finally, Answer 4 is incorrect. 1.41% chose this answer, “Surgical intervention is indicated to resect the liver in the presence of NAFLD.” People with NAFLD and other risk factors, have an increased risk of disease progression to cirrhosis and liver cancer, which might require surgical intervention. However, no surgical intervention is warranted for NAFLD. The cornerstones of treatment for NAFLD are nutrition therapy interventions with a focus on decreasing processed foods, sugary beverages and foods high in saturated fat. Plus, increasing intake of whole foods and committing to a structured physical activity plan to decrease visceral and hepatic adiposity is imperative.
Learn Test-Taking Secrets with Coach Bev – Option to add on 200+ Computerized Practice Test Questions for $49
During this webinar, Coach Beverly will help you transform your nervousness into focused energy that will help you succeed. She will provide test-taking tips based on her experience taking the certification exam six times.
To provide plenty of practice, Coach Beverly will sample 20 test questions that have been plucked from our Test Taking Toolkit during this live webinar.
She will explain how to dissect the question, eliminate wrong answers and avoid getting lured in by juicy answers.
Includes a review of 20 sample test questions with test taking strategies.
This includes access to the recorded version of this webinar on your Online University Student Portal.
Plus, the Test Taking Toolkit provides you with over 200+ sample online practice questions, simulating the exam experience.
A perfect way to assess your knowledge and create a focused study plan, while increasing your test-taking confidence.

Whether you are new to diabetes or a seasoned expert, you’ll benefit from this virtual conference with the latest research plus critical content that you can immediately apply to your clinical practice.
Download Course Flyer
If you are seeking a state-of-the-art review of current diabetes care, this course is for you. Our team has been fine-tuning this course for over fifteen years, and we know what you need. This program can also be a great addition to your CDCES or BC-ADM exam study plan.
Join us LIVE for this Virtual Course and enjoy a sense of community!
Team of expert faculty includes:
Deluxe Option for $449: Virtual Program includes:
Deluxe Version includes Syllabus, Standards and Swag*:
Don’t worry if you can’t make it live. Your registration guarantees access to the recorded version in the Online University.
All hours earned count toward your CDCES Accreditation Information
Sign up for Diabetes Blog Bytes – we post one daily Blog Byte from Monday to Friday. And of course, Tuesday is our Question of the Week. It’s Informative and FREE! Sign up below!
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the CDCES exam. CBDCE does not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the CDCES exam, except for those published by CBDCE.
We have just added this novel, first in class, dual incretin hormone therapy, Tirzepatide (Mounjaro), to our printed version of our Diabetes Medication PocketCard.
This new twin therapy includes not only a GLP-1 Receptor Agonist, but also a Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), which magnifies the therapeutic effectiveness. The SURPASS studies indicate that study participants experienced an A1C drop of up to 2.5% and weight loss of up to 10kg or more.
Incretins (GLP-1 and GIPs) play a major role in glucose regulation post prandially. Incretins are gut hormones that stimulate insulin release from the pancreas when glucose rises in response to food ingestion. They keep blood sugars in check as well as activating the satiety center, to increase the sense of fullness. Incretins slow gastric emptying and also curb post-meal glucagon release, decreasing post prandial glucose spikes. Unfortunately, people with type 2 diabetes, make less than half of the usual amount of the GLP-1 and GIP hormones, which contributes to chronically elevated glucose levels.
To date, therapies that have only included the Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) have demonstrated major success in managing Type 2 DM.
By creating a formulation with BOTH the GIP and GLP incretin hormones, the A1C lowering and weight loss effectiveness has been significantly amplified.
Tirzepatide is a novel synthetic peptide, engineered to provide a once-weekly injectable medication that acts on glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors.
Tirzepatide has been granted FDA approval for treatment of type 2 diabetes based primarily on a series of trials known as SURPASS. The SURPASS 1 trial compared increasing doses to evaluate dose response. The SURPASS 2-5 Trials compared tirzepatide to the GLP-1 semaglutide and to the basal insulins degludec and glargine. In all of the trials, the findings were impressive.
Summary of SURPASS Trials and Results based on Tirzepatide Package Insert.
This once a week injectable is for adults with type 2 diabetes as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control and support weight loss. Tirzepatide is delivered with a single dose prefilled pen.
Starting Dose: 2.5 mg SC every week for 4 weeks initially; THEN increase to 5 mg SC every week. If additional glycemic improvement is needed, increase by 2.5-mg increments after at least 4 weeks at current dose.
Note: The initial 2.5-mg dose is intended for treatment initiation and is not effective for glycemic control
Maximum dose: 15 mg SC qWeek
Common Adverse Side effects: Nausea, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort and injection site hypersensitivity reactions. There is also a black box warning to avoid if family history of medullary thyroid tumor and to report any signs of pancreatitis immediately.
Cost: Tirzepatide is comparably priced to other GLP-1 RAs on the market at $974.33 for four weekly doses, regardless of dose size. Hopefully, insurance companies will recognize the long term benefits of these newer classes of agents, and increase coverage of these beneficial treatment options.
In conclusion: This new medication class substantially lowers blood sugars and body weight, with a once a week injection. Coupled with healthy eating and keeping active, people with diabetes have the opportunity to improve their health and quality of life with this novel medication class.
Author’s note: Beverly Thomassian has no conflict of interest to report and distilled the content of this article from the SURPASS study results and the tirzepatide package insert.
*PocketCardsTM are for individual use only.

MR is 13 years old, and went to urgent care because they weren’t feeling well and told the Provider “I feel so tired all the time and I have to go the bathroom a lot”. The provider draws labs and gets a urine sample. The A1C is 8.7% with some ketones in the urine. The antibody results aren’t back yet. Based on the ADA Standards and this information, what is the best action?
Click Here to Test your Knowledge
Learn Test-Taking Secrets with Coach Bev – Option to add on 200+ Computerized Practice Test Questions for $49
During this webinar, Coach Beverly will help you transform your nervousness into focused energy that will help you succeed. She will provide test-taking tips based on her experience taking the certification exam six times.
To provide plenty of practice, Coach Beverly will sample 20 test questions that have been plucked from our Test Taking Toolkit during this live webinar.
She will explain how to dissect the question, eliminate wrong answers and avoid getting lured in by juicy answers.
Includes a review of 20 sample test questions with test taking strategies.
This includes access to the recorded version of this webinar on your Online University Student Portal.
Plus, the Test Taking Toolkit provides you with over 200+ sample online practice questions, simulating the exam experience.
A perfect way to assess your knowledge and create a focused study plan, while increasing your test-taking confidence.

This course includes updated goals and guidelines for children living with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. This course discusses the special issues diabetes educators need to be aware of when working with children with diabetes and their families. We discuss the clinical presentation of diabetes, goals of care, and normal growth and development through the early years through adolescence. Strategies to prevent acute and long term complications are included with an emphasis on positive coping for family and child with diabetes.
Objectives:
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the CDCES exam. CBDCE does not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the CDCES exam, except for those published by CBDCE.

We are excited to announce the FDA approval of a novel dual incretin injectable. The SURPASS clinical trials confirm this new diabetes medication not only drops A1C, but also contributes to significant weight loss. We have updated the electronic versions of our Medication PocketCards to include this “first in class” therapy. You can read more in our article below.
June also celebrates Pride Month. Members of the LGBTQ+ community often suffer worse health outcomes and may avoid seeking needed health care due to discrimination or discomfort within the current health care model. We explore strategies to increase inclusion and embrace diversity in diabetes care and beyond.
Our next article explores if intermittent fasting results in weight loss. We highlight the findings of a recently published randomized trial that provides some unexpected findings.
Lastly, we are excited to share a bunch of free resources and webinars with you. You can download our new diabetes self-care cheat sheet in Spanish, plus join us for 3 Free Webinars. These free courses with Coach Beverly include Test Taking Success, CDCES, and BC-ADM Prep Webinars.
Don’t forget to check out our Question and Rationale of the week. We think you will find them interesting and informative. We also love sharing this picture of Amanda, our Logistics Assistant, holding a colorful bundle of newly finished pancreas partners
We thank you for being a light to people living with diabetes. You are touching the lives of many through your care!
Beverly, Bryanna, Jackson, and Amanda
Featured Articles
Upcoming FREE Webinars
Featured Items
Learn Test-Taking Secrets with Coach Bev – Option to add on 200+ Computerized Practice Test Questions for $49
During this webinar, Coach Beverly will help you transform your nervousness into focused energy that will help you succeed. She will provide test-taking tips based on her experience taking the certification exam six times.
To provide plenty of practice, Coach Beverly will sample 20 test questions that have been plucked from our Test Taking Toolkit during this live webinar.
She will explain how to dissect the question, eliminate wrong answers and avoid getting lured in by juicy answers.
Includes a review of 20 sample test questions with test taking strategies.
This includes access to the recorded version of this webinar on your Online University Student Portal.
Plus, the Test Taking Toolkit provides you with over 200+ sample online practice questions, simulating the exam experience.
A perfect way to assess your knowledge and create a focused study plan, while increasing your test-taking confidence.
Sign up for Diabetes Blog Bytes – we post one daily Blog Byte from Monday to Friday. And of course, Tuesday is our Question of the Week. It’s Informative and FREE! Sign up below!
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the CDCES exam. CBDCE does not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the CDCES exam, except for those published by CBDCE.

For last week’s practice question, we quizzed test takers on complications of hyperglycemia during pregnancy. 60% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question
Question: AR has type 1 diabetes and is in shock because they just discovered they are 6 weeks pregnant. AR uses a CGM and insulin pump to manage their diabetes and their most recent A1C is 8.3%. Which of the following is a potential complication associated with hyperglycemia during the first 10 weeks of pregnancy?
Answer Choices:
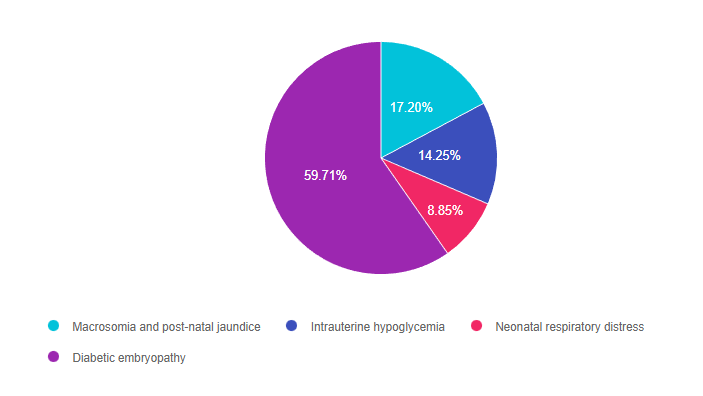
As shown above, the most common choice was option 4, the second most common answer was option 1, then option 2, and finally 3.
Answer 1 is incorrect. 17.20% chose this answer, “Macrosomia and post-natal jaundice.” This is a juicy answer since macrosomia and post natal jaundice are often associated with gestational diabetes (GDM) However, this question is not asking about GDM, which is usually diagnosed between 24-28 weeks of pregnancy. In this question, AR already has type 1 when becoming pregnant and wants to know the consequence of hyperglycemia during the first 10 weeks when the fetal organs are developing.
Answer 2 is incorrect. 14.25% of you chose this answer, “Intrauterine hypoglycemia.” This answer is designed to lure the test taker in with the word hypoglycemia. A fetus who is exposed to excess glucose in utero is at risk of post natal hypoglycemia AFTER delivery, since they no longer are receiving maternal glucose and their pancreas is making abundant insulin. A fetus exposed to excess intrauterine glucose levels is at risk of hyperglycemia (not hypo).
Answer 3 is incorrect. 8.85% of respondents chose this answer, “Neonatal respiratory distress.” This is a juicy answer since neonatal respiratory distress is often associated with GDM and diabetes in pregnancy. However, this question is not asking about post delivery complications. In this question, AR already has type 1 when becoming pregnant and wants to know the consequence of hyperglycemia during the first 10 weeks when the fetal organs are developing.
Finally, Answer 4 is correct. 59.71% chose this answer, “Diabetic embryopathy.” Yes, GREAT JOB, this is the best answer. The first trimester of fetal development is when the organs are developing. A fetus exposed to excess levels of glucose during this critical time is at increased risk of congenital defects like anencephaly, microcephaly, neural tube defects and others. For people with diabetes, achieving an A1C of less than 6.5% before conceptions improves outcomes and decreases risk of congenital anomalies. With careful planning and keeping a close connection with their health care team, people with diabetes can experience healthy pregnancies and great outcomes.

Pregnancy with diabetes is confronted with a variety of issues that require special attention, education, and understanding. This course reviews those special needs while focusing on Gestational Diabetes and Pre-Existing Diabetes. Included are the most recent diagnostic criteria, management goals, and prevention of complications during pregnancy. A helpful review for the CDCES Exam and for those who want more information on people who are pregnant and live with Diabetes.
Objectives:
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the CDCES exam. CBDCE does not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the CDCES exam, except for those published by CBDCE.
Last week, I attended my 17-year-old son’s band and theater high school award ceremony. In addition to the cultural diversity of these gifted teenagers, there were a number of award recipients from the lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ+) community. Each individual was celebrated and cheered on by their peers and recognized for their unique talents. As I left the auditorium, my heart was filled with joy knowing that there is room for everyone to share their gifts. This event was so much more enlightened compared to my high school experience over 30 years ago.
I am thrilled that the public high school in our community is taking steps to increase inclusivity for the LGBTQ+ community, but we have a long way to go in making other public spaces and health care settings welcoming for all.
According to an article recently published in ADCES in Practice, “Know Thyself, A Cultural Humility Framework for Diabetes Education for LGBTQ+ Individuals”, authored by Katie Savin and Theresa Garnero, the LGBTQ+ population continues to experience worse health outcomes than their heterosexual and cis counterparts. This discrimination is amplified in communities of color.
Health and Diabetes Disparities
In their article, Garnero and Savin highlight that members of the LGBTQ+ community are less likely to have health insurance and experience higher rates of food insecurity. LGBTQ+ adults are also vulnerable to poor physical and mental health. Membership in a stigmatized community puts LGBTQ+ adults of all ages at greater risk for engaging in behaviors such as smoking, substance misuse and binge eating. Experts suggest that the Minority Stress Model, which includes the LGBTQ+ community, increases sexual and gender minorities risk for mental illness, anxiety, depression and risky health behaviors.
Create health care settings that send a message of welcomeness to the LGBTQ+ community. There are many small and big ways to send a message of inclusion.
Cultural humility asks health care providers to develop critical self-awareness of personal implicit or explicit values that and behaviors that may contribute to health care disparities. Cultural humility acknowledges the role of power and privilege within the patient-provider dynamic and within the health care system itself. Cultural values and behaviors emanating from the provider actually have the power to shape the encounter and may minimize the values of the person seeking care. By taking a closer look at our own biases during interactions, we can start becoming more intentional and align with the individual’s needs and values when providing care.
Get comfortable with the language of LGBTQ+
Inclusive language creates a bridge and the foundation of trust between health care provider and participant. Challenge yourself to adopt inclusive language practices by taking time to learn the terminology. Make sure intake forms include same-gender parenting, same-gender partnerships and non-binary gender options.
To get more comfortable with the language culture of LGBTQ+ community members, consider challenging your healthcare setting to integrate LGBTQ+ cultural events and practices in the work setting.
As individuals, we can visit a local LGBTQ+ Center, attend a pride march, drag show or other event that provides acculturation to the community’s customs. Plus, you’re likely to have fun in the process.
Increasing exposure to the LGBTQ+ community helps decrease discomfort and improves the quality of your interactions when providing care. In addition, since members of the LGBTQ+ are at higher risk for mental health distress, make sure to assess for anxiety, depression and drug misuse.
We enrich our practice when we welcome people from diverse communities and backgrounds. Let’s make sure to let our LGBTQ+ community know they are safe with us.
List of Resources
ADCES Inclusive Care for LGBTQ+ People with Diabetes Handout – this handout provides definitions, terms to avoid, and a cultural competency checklist to help you move towards improving inclusivity within your practice.
All Gender Restroom Sign PDF
Diabetes Prevention and Management for LGBTQ+ People Handout – this handout includes research of diabetes within the LGBTQ+ community, along with clinical considerations, programs, and resources for diabetes educators to use within their practice.
Policies on Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender & Queer (LGBTQ+) issues – this resource by the American Medical Association lists all the current healthcare policies in place for the LGBTQ+ community.
Helio’s LGBTQ+ Health Updates Resource Center – this is a “collection of news articles and features that provide the latest information on the unique health needs of individuals in the LGBTQ+ community.”
This bundle includes our CDCES Online Prep Bundle plus the ADCES Review Guide.
The online bundle includes Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 (Boot Camp), plus two bonus courses. The ADCES Review Guide offers over 480+ practice questions and is a fantastic independent study tool and comprehensive resource for the Diabetes Care and Education Specialist Exam.
Read More: What is a CDCES? First awarded in 1986, as Certified Diabetes Educator (CDE) credential and in 2020 with a new name: Certified Diabetes Care and Education Specialist (CDCES) to more accurately reflect the specialty. CDCES has become a standard of excellence for the delivery of quality diabetes education. Those who hold this certification are known to possess comprehensive knowledge of and experience in diabetes prevention, management, and prediabetes. “Becoming a Certified Diabetes Care and Education Specialist (CDCES) is one of the best professional and personal decisions I have ever made.” – Coach Beverly Thomassian, RN, MPH, CDCES, BC-ADM 
Read More: 3 Reasons to Become a CDCES “The best part of becoming a CDCES is working with my colleagues and people living with diabetes. As diabetes educators, we hear compelling and beautiful life stories. I am astounded by the barriers they face and inspired by their adaptability, problem-solving skills, and resilience.” Reason 1: CDCES is a widely recognized certification by employers and health care professionals throughout the U.S. This credential demonstrates a specialized and in-depth knowledge in the prevention and treatment of individuals living with pre-diabetes and diabetes. Reason 2: Currently, 10% of people in the U.S. have diabetes and another 35% have pre-diabetes which means 45% of Americans are running around with elevated blood glucose levels. Given this epidemic, there will be plenty of future job opportunities. Reason 3: Having my CDCES along with my nursing degree, has opened many doors of opportunity; from working as an inpatient Diabetes Nurse Specialist in a hospital to working as a Manager of Diabetes Education in the outpatient setting to starting my own consulting company.
Sign up for Diabetes Blog Bytes – we post one daily Blog Byte from Monday to Friday. And of course, Tuesday is our Question of the Week. It’s Informative and FREE! Sign up below!
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the CDCES exam. CBDCE does not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the CDCES exam, except for those published by CBDCE.

45 to 75% of individuals with type 2 diabetes have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). NAFLD has associated with an increased risk of steatohepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Which of the following statements is true based on ADA Standards of Care?
Click Here to Test your Knowledge
Learn Test-Taking Secrets with Coach Bev – Option to add on 200+ Computerized Practice Test Questions for $49
During this webinar, Coach Beverly will help you transform your nervousness into focused energy that will help you succeed. She will provide test-taking tips based on her experience taking the certification exam six times.
To provide plenty of practice, Coach Beverly will sample 20 test questions that have been plucked from our Test Taking Toolkit during this live webinar.
She will explain how to dissect the question, eliminate wrong answers and avoid getting lured in by juicy answers.
Includes a review of 20 sample test questions with test taking strategies.
This includes access to the recorded version of this webinar on your Online University Student Portal.
Plus, the Test Taking Toolkit provides you with over 200+ sample online practice questions, simulating the exam experience.
A perfect way to assess your knowledge and create a focused study plan, while increasing your test-taking confidence.

Whether you are new to diabetes or a seasoned expert, you’ll benefit from this virtual conference with the latest research plus critical content that you can immediately apply to your clinical practice.
Download Course Flyer
If you are seeking a state-of-the-art review of current diabetes care, this course is for you. Our team has been fine-tuning this course for over fifteen years, and we know what you need. This program can also be a great addition to your CDCES or BC-ADM exam study plan.
Join us LIVE for this Virtual Course and enjoy a sense of community!
Team of expert faculty includes:
Deluxe Option for $499: Virtual Program includes:
Deluxe Version includes Syllabus, Standards and Swag*:
All hours earned count toward your CDCES Accreditation Information
Sign up for Diabetes Blog Bytes – we post one daily Blog Byte from Monday to Friday. And of course, Tuesday is our Question of the Week. It’s Informative and FREE! Sign up below!
The use of DES products does not guarantee the successful passage of the CDCES exam. CBDCE does not endorse any preparatory or review materials for the CDCES exam, except for those published by CBDCE.