“Savory Foods May Help Promote Healthy Eating”
Humans are said to have five basic tastes: salty, sweet, bitter, sour, and the least known, umami. Umami is a Japanese word “used to express a delicious, savory meal.” Recent studies are beginning to show that healthy eating habits may be influenced by consuming savory foods.
Glutamate, a key component of Umami taste, is an amino acid that is commonly found in savory foods with higher protein values. Previous studies have shown that consuming glutamate via broth can decrease overall appetite and intake. This is especially helpful for individuals who struggle with overeating and weight gain. A study by the Journal of Neurophyschopharmacology found that the participants, “had more focused gazes during the meal and had more engagement of a brain area that is linked to successful self-regulation during food choice.”
Further research may help encourage and facilitate healthier eating patterns and reduce the amount of individuals at risk for developing type 2 diabetes and becoming obese.
To learn more about Umami and its prevalence in weight loss and appetite control, visit Savory Foods May Help Promote Healthy Eating.
“Children who drink fruit juice with breakfast are 50% more likely to be overweight”
“Children who drink fruit juice with breakfast are more likely to become overweight or obese.”
A recent study by the Medical University of Vienna reported that “children who had orange or apple juice with their breakfast were 50% more likely to be overweight.” On the alternative end, the children consuming water in the study decreased their risk for obesity by 40%. The study also evaluated the children’s overall eating habits and whether or not they skipped breakfast. The study found that the children who ate breakfast every morning were generally three pounds lighter than the children who skipped it all together.
The experts in the study recommended to look for fruit juices with lower added sugar and very simple ingredients. The increased risk of obesity is likely due to the the added sugars as well as the overall higher energy content. A small glass of freshly squeezed orange juice with no added sugar is a better, low-calorie option since it contains beneficial vitamins and minerals that are vital for children’s development. The fiber content in natural fruit juices is also beneficial for promoting good digestive health. Of course, enjoying the whole fruit is always the best option.
In summary, fruit juice does not necessarily need to be eliminated altogether. Consider it a special treat. But better choices include eating the fruit instead or diluting the juice with 50% water (sparkly water works great) to decrease overall sugar and energy content.
To read more about this topic, visit Children who drink fruit juice with breakfast 50% more likely to be overweight.
Written by: Sofia Sepulveda
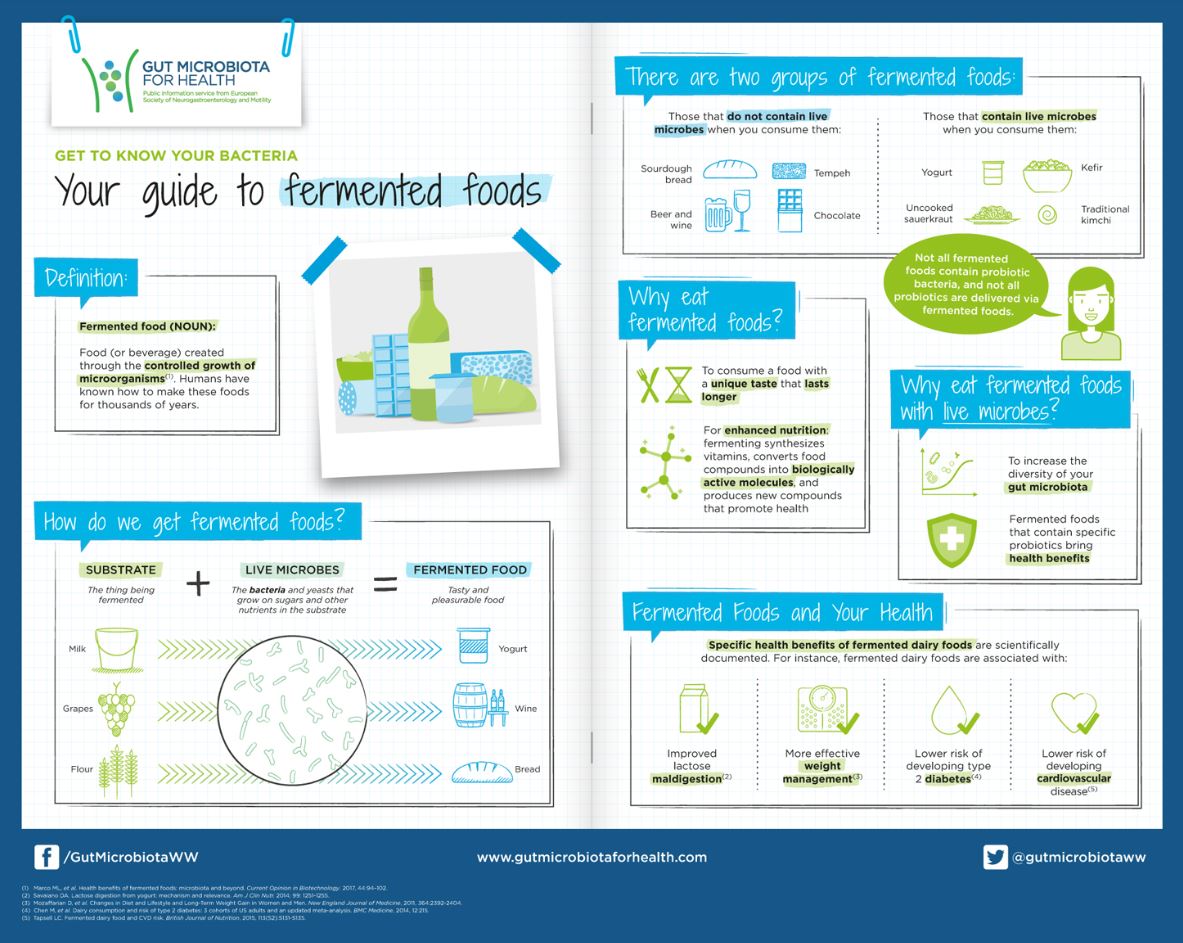
Fermented Foods Guide to Boost Microbiota Health
Maintaining a wide diversity of gut microbiome is vital for good health. A large amount of these microbes can be acquired through fermented foods like yogurt, kombucha, and sauerkraut. Fermented foods and the microbes they provide have proven to improve digestion of lactose, aid in weight management, lower risk of type 2 diabetes, and lower risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
This guide to fermented foods provides a quick and dirty guide to increasing gut bacteria diversity and through fermented foods.
Want to learn more? Join the wonderment as we explore the role of our Microbiome with our “New Horizons – Getting to the Gut” webinar
Join us to learn about the exciting advances in our understanding of the pathology of diabetes and novel approaches to prevention. We will discuss trends in diabetes diagnosis and classification. The role and importance of gut bacteria in the pathology of type 1 and type 2 will explored. A detailed discussion on emerging research and clinical trial on interventions to delay or prevent diabetes is also included.
Topics Include:
- Describe trends in diabetes
- Discuss current research in the importance of gut bacteria.
- Describe 2 interventions to delay or prevent diabetes
“Pre-workout breakfast could prime body to burn carbs”

Many people wonder if they should eat breakfast before working out or hold off on consuming calories until after exercise. Recent research by the University’s Department for Health at the universities of Birmingham, Newcastle, and Stirling has shown that the pre-workout breakfast can actually increase post meal glucose utilization.
In this study, 12 healthy males were given a control breakfast and were required to rest for three hours prior to exercise. Blood glucose levels and muscle glycogen levels were then tested post exercise and rest. Researchers found that consuming breakfast actually made the body more effective at burning carbohydrates during exercise, “as well as increasing the rate the body digested and metabolised food eaten after exercise too.”
They compared the results to participants who skipped breakfast. The researchers found that fasting before exercise actually had the opposite effect and made the body far less efficient at burning carbohydrates during exercise. Researchers also discovered that the subjects were not only burning carbohydrates from their breakfast but from their muscle glycogen stores as well. This provides explanation for why there is rapid clearance of blood sugar after lunch.
This study has only assessed short term effects. Therefore, further research must be performed to discover long term implications.
To learn more about carbohydrate metabolism, visit Eating breakfast burns more carbs during exercise and accelerates metabolism for next meal.
Contributed by Sofia Sepulveda
Food truck puts reservation on road to better health
 30% of American Indians on the White Earth Reservation have Type 2, which is three times the national average.
30% of American Indians on the White Earth Reservation have Type 2, which is three times the national average.
Accessibility to fresh fruits and vegetables plays an integral role in a community’s health. Often we stumble upon “food deserts – regions where grocery stores with fresh, healthy options simply don’t exist.”
This summer, a new food truck has set out to make healthy eating more accessible to those who are not near grocery stores. White Earth Nation purchased a “healthy” food truck to help tribal members have access to healthy, locally produced and traditional foods.
Unhealthy eating habits are often tied to generations with limited access to fresh foods and can lead to chronic long-term health problems.
The goal of the new food truck is to provide more choices, as the White Earth Food truck travels to reservation villages in the summer with fresh produce and in the winter with other foods like squash, wild rice and preserves made from summer crops.
To learn more about the new food truck – White Earth hopes food truck puts reservation on road to better health by MPRnews
Please also enjoy our Plant Based Resource page
“These four foods are proven to lower your cholesterol”

The “Plant-based movement” has gained increasing popularity within the past few years, with more people turning to fruits and vegetables to help improve their health. As interest increases, as does research. A study conducted suggest four main foods that can have big benefits to the heart, such as lowering your cholesterol and blood pressure!
The fours foods said to benefit cholesterol include:
- Nuts
- Plant Protein such as tofu, soy milk, beans, peas, chickpeas, etc,.
- Soluble fibers such as oats, eggplant, apples, oranges
- Margarine enhanced with plant sterols, or “cholesterol-like” compounds that can be found in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and cereals
Multiple governmental organizations such as the European Association for the Study of Diabetes are beginning to recognize and further investigate this particular diet as a prevention plan for cardiovascular diseases.
Particularly the recommended foods above, called the “Portfolio” diet, which includes an intake of 42 grams of nuts, 20 grams of soluble fiber, 2 grams of plant sterols, and 50 grams of plant protein. The study concluded, “overall, the analysis found that sticking to the Portfolio diet lowers total cholesterol levels, as well as triglycerides (which are the most common fat types in the human body), blood pressure, and C-reactive protein (which is a marker of inflammation).”
As research continues, we are seeing more and more evidence that a plant-based diet is not only restorative to your health, but can also be preventative.
Check out additional Plant Based Eating Resources here.
You can learn more – “These four foods are proven to lower your cholesterol” by Medical News Today
Breast milk feeds good gut bacteria and reduces obesity
 By: Sofia Sepulveda
By: Sofia Sepulveda
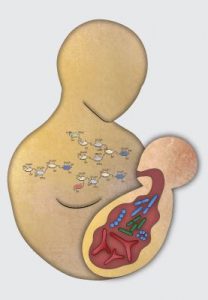
A recent study by the Department of Pediatrics and Child Health has found that breastfeeding has a major impact on the kind of gut bacteria that a baby develops. Babies that were breastfed in this study showed to have more beneficial gut bacteria that decreases risk of obesity in their future.
Breast milk plays a critical role in the present and future health of an individual. Breast milk ” contains, oligosaccharides which are complex sugars that feed specific gut bacteria.” It specifically fed the good bacteria in the gut that has a positive effect on how fat is stored and burned. These oligosaccharides are not present in infant formula. This may contribute to increased weight and risk of obesity for formula fed babies.
This particular study assessed over 1,000 infants during their first year of life. Stool samples were taken during month 3 and month 12 and were used to test for gut bacteria diversity. Weight differences became apparent around the 3 month mark, as the babies receiving formula were typically overweight or at risk. Only 19 percent of the babies who were breastfed were overweight or at risk compared to 33 percent of the formula fed babies.
The research emphasizes that breastmilk has “many important bioactive components that influence appetite and weight gain, including growth factors and hormones, which are not present in infant formulas.” This weight difference is most likely due to the nutrients contained in breast milk that are not found in formula.
Microbes have a very special role in the way that we digest food. Individuals accumulate these microbes in many different ways and may be affected by, “the type of delivery, whether the baby or mother gets antibiotics, and what the baby is fed and when solid foods are introduced.” Not having a healthy array of microbes is associated with weight gain and increased the likelihood of obesity during infancy.
 For more information, visit “Infant formula could change gut bacteria, contribute to childhood obesity”
For more information, visit “Infant formula could change gut bacteria, contribute to childhood obesity”
To help get the word out visit World Breast Feeding Week Resource Page
You can also learn more about Women and Diabetes with our webinar below or via the “Women and Diabetes Resource Page”
“Nutrition tips to promote wound healing”
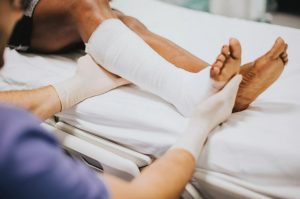 In healthy individuals, wounds can heal fairly quickly and easily due to our bodies natural ability to continuously produce new cells. Wounds that involve medical intervention, such as decubutis ulcers, require a bit more time and care for optimal healing. Diabetic ulcers are a huge issue for individuals with diabetes who are bedridden or use wheelchairs. They are also known as “pressure sores” or “bed sores” and form where bones are closer to the skin. These ulcers are specifically problematic to the foot area and may take a significant amount of time to heal.
In healthy individuals, wounds can heal fairly quickly and easily due to our bodies natural ability to continuously produce new cells. Wounds that involve medical intervention, such as decubutis ulcers, require a bit more time and care for optimal healing. Diabetic ulcers are a huge issue for individuals with diabetes who are bedridden or use wheelchairs. They are also known as “pressure sores” or “bed sores” and form where bones are closer to the skin. These ulcers are specifically problematic to the foot area and may take a significant amount of time to heal.
Food and nutrition plays a huge role in wound healing. The vitamins, minerals, and energy that we consume are vital for proper healing. Nutrient intake is especially important due to the great loss of nutrients that are lost in the blood supply exiting the wound.
To increase efficiency of wound healing, it is important to consume a sufficient amount of calories from whole foods. Refer to the My Plate Guidelines, for tips on creating a healthy and balanced meal. Adequate protein intake is also very beneficial.
Encourage people with diabetes and ulcerations to try to consume around 10-20 grams of protein with each meal or snack to ensure recovery. Strategies to increase protein intake could include, adding eggs to breakfast, peanut butter or chia seeds to a morning smoothie. Some herbs or spices, such as turmeric, may aid in fighting inflammation as well.
Assessing vitamin and mineral intake is vital, as many nutrients are lost through the wound. It is recommended to consult with a dietitian to assess specific nutrient needs. A dietitian with a background in diabetes may also be helpful in developing a nutrition plan to help control blood sugar levels and aid in wound healing.
For more information on nutrition and wound healing, visit 5 Nutrition Tips to Promote Wound Healing.
For more information on foot ulcers, be sure to check out our Foot Examination Pocket Chart.