
Subscribe
eNewsletter

Ready to get certified?
Free CDCES Coach App
Download
Free Med Pocket Cards

eNewsletter

Free CDCES Coach App
Free Med Pocket Cards
Dr. Banting was born on November 14, 1891. That is why we celebrate World Diabetes Day on November 14th.
On October 25th, 1923 the Nobel prize in physiology or medicine was awarded to Frederick Grant Banting and John James Richard MacLeod “for the discovery of insulin”. The discovery was made in 1921, which makes the two-year time period between the detection and this prize one of the shortest in the history of the Nobel Prize.

During a hot summer in 1921, Dr. Banting secured space to test out his theory in the University of Toronto. Along with his colleague, Charles Best, and a bare bones lab, they conducted dozens of experiments on dogs, which ultimately led to the discovery of insulin.
Dr. Banting and Charles Best began their experiments ligating the pancreases of dogs, thinking this would prevent destruction by the digestive pancreatic juices, and then isolating the extract from the islet cells. They then processed the extract from the islet cells and injected this extract they called “insulin” into diabetic dogs. According to an audio Interview with Dr. Best, by July 1921, they had 75 positive examples of insulin lowering blood glucose levels in dogs.

In February 1922, doctor Frederick Banting and biochemist John Macleod published their paper on the successful use of a alcohol based pancreatic extract for normalizing blood glucose levels in a human patient.
Here are some photos of the first insulin bottles produced by the University of Toronto and Eli Lilly.
Soon, word of their discovery got out and the race was on to produce enough insulin to treat the flood of type 1 patients arriving in Toronto to receive this miracle injection.
First Children to Receive Insulin

The first patient to receive insulin was a ‘welfare’ case at Toronto General Hospital – no clinical trial structure to say the least. People from Canada/US flooded into Toronto to receive treatment. Banting struggled with the lack of accessibility of insulin – volume needed and issues of purification.
The earliest patients were “selected”, some youths from Canada/US, some soldiers with diabetes (probably because of Banting’s service in the First World War) and then later some select private patients. During this time they were working hard to increase the volume and continue to improve the purification process. Insulin was available for testing in US, namely through Dr. Elliot Joslin in the late summer 1922.
Dr. Banting – Fun and Interesting Facts

Takes a Team
While Best played a critical and important role, credit must also go to Professor Macleod, from the University of Toronto, who provided the lab space, showed Dr. Banting how to operate on dogs, provided his student Best and suggested they switch from a saline to alcohol to purify the ‘extract’. Dr. Macleod also secured the support of JB Collip, the 4th man on the team and the fist person to purify insulin for human use. Best is also known for pushing Banting to return to the research during a particular dark period of failure.
Historical Insulin Powerpoint Slides – here is a collection of some of my favorite powerpoint slides, depicting the discovery of insulin.
Visit Banting House Facebook Page
Canadian Broadcast that highlights the first patient, Ted Ryder, the first patient to receive insulin from Dr. Banting. Some great historic video footage of Dr. Banting shaking hands with the young man..
The Quest – 1958 This short film is a re-enactment of the critical year in Dr. Frederick Banting’s life when he discovered insulin for the treatment of diabetes at the University of Toronto. It depicts the odds against which he and his assistant, Charles Best, worked; the scepticism of other doctors and the final victory that gave thousands of diabetics hope for a healthier life.
The Flame – Banting House Historical Site Newsletter
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on Gestational Diabetes: Diabetes Care in the Fourth Trimester. 51% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

MT is a 29-year-old with Type 1 diabetes who is currently 14 weeks pregnant. She uses a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) with concurrent fingersticks and uploads her glucose data weekly. Her CGM settings was already set to the recommended time in
range and the latest CGM report shows the following: time in range (TIR): 67%, time below range: 6%, time above range: 27%.
Based on current ADA Standard of Care, which of the following statements is most accurate regarding her CGM values?
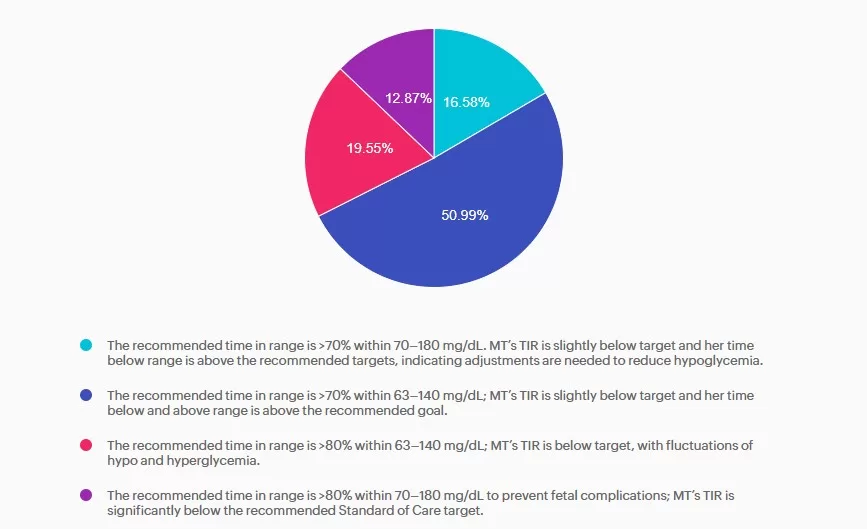
Answer A is incorrect: 16.58% chose this answer, “The recommended time in range is >70% within 70–180 mg/dL. MT’s TIR is slightly below target and her time below range is above the recommended targets, indicating adjustments are needed to reduce hypoglycemia.” Answer A is incorrect. The answer uses non-pregnancy CGM target range of 70–180 mg/dL. Pregnancy target range for individuals with type 1 diabetes are lower, keep reading for the best answer.
Answer B is correct: 51% chose this answer, “The recommended time in range is >70% within 63–140 mg/dL; MT’s TIR is slightly below target and her time below and above range is above the recommended goal.” Answer B is correct. Based on the 2025 ADA Standards of Care the recommended time in range targets for individuals with type 1 diabetes during pregnancy is >70% between 63-140 mg/dL, < 4% under 63 mg/dL with < 1 % under 54 mg/dL, and < 25% over 140 mg/dL.
Answer C is incorrect: 19.55% chose this answer, “The recommended time in range is >80% within 63–140 mg/dL; MT’s TIR is below target, with fluctuations of hypo and hyperglycemia.” Answer C is incorrect. The time in range target is above the evidenced-based
minimum and MT is having frequent hypoglycemia in addition to hyperglycemia, both outside the goal ranges.
Answer D is incorrect: 12.87% chose this answer, “The recommended time in range is >80% within 70–180 mg/dL to prevent fetal
complications; MT’s TIR is significantly below the recommended Standard of Care target.” Answer D is incorrect. The recommended target range for individuals with type 1diabetes during pregnancy is 63-140 mg/dL as stated above.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!
with Coach Beverly Thomassian RN, MPH, CDCES, BC-ADM
Course credits through AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™, ACPE, ANCC, and CDR!
This course is included in our Level 2 | Standards of Care Intensive
This Level 2 course fulfills the annual ADA Standards of Care component required for CDCES certification renewal. They also count toward your CDCES and BC-ADM certification CE requirements.

Join Coach Bev for an in-depth exploration of the 2026 ADA Standards! This is our most popular course of the year, offering the perfect opportunity to immerse yourself in the essential content featured in this comprehensive 300-page clinical guidebook.
This course, updated annually, is an essential review for anyone in the field of diabetes. Join Coach Beverly as she summarizes the annual updates to the American Diabetes Association’s (ADA) Standard of Medical Care in Diabetes. This course provides critical teaching points and content for healthcare professionals involved in diabetes care and education.
Topics:
Course Objectives:
Upon completion of this activity, participants will be able to:

The fourth trimester describes the time from delivery through the first 12 weeks postpartum. During this phase, attention often shifts to the newborn. However, for those who experienced gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), engaging with their health care team can set the stage for long-term health and well-being.
Although only about 10% of individuals are affected by GDM, their risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases tenfold after delivery¹. Despite this heightened risk, studies ²,³ demonstrate that postpartum follow-up remains suboptimal. Comprehensive postpartum care planning started before delivery supports physical and psychological health for the long run
Individuals with GDM usually transition off diabetes medications in the postpartum period ¹; however, it is important to ensure appropriate medication care plans are in place based on the individual’s need. As prior existing pre-diabetes or diabetes may be found in up to one-third ² of individuals during this stage, both the American Diabetes Association and ACOG recommend oral glucose tolerance testing (OGTT) using pre-pregnancy criteria at 4-12 weeks 3 after delivery. OGTT is recommended instead of A1c testing, within the first 12 weeks postpartum, because of changes in blood volume, blood loss during delivery, and the rapid glycemic variations after birth.
However, we know barriers follow-up care and screenings exist. One health system’s retrospective study ¹ showed that while most women receive care from an OB-GYN after delivery, only 29% completed the recommended blood glucose screening. Among those
with abnormal results, just 11% were prescribed glucose-lowering medications, and 21% received a referral for diabetes risk reduction. This study is not unique ¹,² in its findings, and it highlights the need for proactive outreach and post-delivery care.
Ongoing and additional screenings are recommended due to increased cardiometabolic health risks. If postpartum OGTT results are found normal, repeat pre-diabetes and diabetes screening is recommended at least every 1-3 years. ¹ Home blood pressure monitoring is recommended for individuals with history of hypertension. Checking a lipid panel within the first year postpartum for assessment of ASCVD risk, however lipid levels may take up to 3 months to return to pre-pregnancy levels and should not be performed before 6 weeks postpartum due to pregnancy-related changes in lipid metabolism. Routine screening for post-partum depression is also recommended, given the higher prevalence of depression symptoms during and post-GDM, impacting self-care and metabolic outcomes.
In addition to early screening, intervention strategies require a multidisciplinary approach focusing on recovery, prevention, and empowerment. Coordination between OB-GYN, primary care, diabetes care teams, and pediatric groups ensures continuity of care. Education on lifestyle and behavioral health management should be delivered with empathy and flexibility, recognizing the competing demands of new motherhood. A Diabetes Prevention Program subgroup analysis of women who received lifestyle
interventions 10 years after GDM found a 50% decreased incidence of development of diabetes, and a more recent meta-analysis 5 found lifestyle interventions reduced the incidence of diabetes by 24%. Interventions with a registered dietitian can support lactation, restore nutrient balance, and promote cardiometabolic risk reduction.
Encouraging a gradual return to physical activity, beginning with gentle movement and progressing to regular moderate exercise, is associated with improved insulin sensitivity, diabetes risk reduction, and enhanced mood. Incorporating lactation consultants into postpartum care supports ACOG recommendations for exclusive breastfeeding the first 6 months of life and continued up to 2 years of age with solid foods transition. Though challenges such as delayed milk production and reduced supply may occur 6 due to the history of insulin resistance, breastfeeding offers many health benefits and significantly lowers the risk of developing type 2 diabetes for both mother and child. 4 Finally, establishing a clear transition plan to primary care that promotes annual visits, family planning, and ongoing lifestyle support may enhance long-term health maintenance.
Flexible care delivery models that meet women where they are in this stage of life may further help overcome barriers and reduce disparities in postpartum follow-up.
The fourth trimester represents a pivotal opportunity to ensure postpartum care and support to engage lifelong health. This time often shifts focus to the newborn, but for women with a history of GDM, this period is not only about recovery but also prevention of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and future pregnancy complications. The diabetes care team can support postpartum screenings, nutrition, lifestyle interventions, and transition of care that close postpartum care gaps. Proactively outreaching and engaging during this critical phase can connect individuals to resources and long-term chronic disease prevention.
References:

JR was recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, but based on their history of pancreatitis, you suspect JR actually has Diabetes Type 3c.
Which of the following symptoms match a diagnosis of Diabetes Type 3c?
Level 5 | From the Gut to the Butt – Exploring the GI System

Use the code Cyber30 for 30% off at checkout!

Featured Articles ___________________________ |
Upcoming Programs ___________________________ Upcoming FREE Webinars ___________________________ |
Greetings, wonderful healthcare colleagues!
Did you know that over 16% of American adults—nearly 1 in 6—are living with diabetes, according to the latest data from the CDC? When we look at the bigger picture, it becomes clear that social drivers of health play a decisive role in this growing epidemic.
Data suggests that access to knowledge, resources, and supportive environments can profoundly impact prevention, diagnosis, and daily diabetes management. By equipping individuals with knowledge about diabetes management and preventative measures, we empower them to take ownership of their health and inspire change within their communities.
To get the ball rolling, we are excited to share a list of our favorite FREE diabetes resources in English and Spanish. Please share this information with your colleagues and community members.
Have you considered the implications of Stage 4 Gestational Diabetes (GDM)? As Christine Craig highlights, after the birth of a baby, it is challenging to keep follow-up appointments and receive ongoing healthcare. Yet after delivery with GDM, the risk of future diabetes is high, and staying connected with the care team improves outcomes. Read more about this critical 4th Stage.
Our tech expert, Dr. Sarah, considers the impact of technology on diabetes distress. What effect does being “plugged” into technology have on the emotional health of the person living with diabetes?
Lastly, to help everyone feel their best this holiday season, we are sharing our popular handout, “Ten Strategies to Survive the Holidays” as well as an info sheet on reframing diabetes distress.
We hope you can join our FREE webinars celebrating National Diabetes Month. We sincerely appreciate your ongoing dedication to improving diabetes care.
With gratitude for the care you give every day!
Coach Beverly, Bryanna, Astraea & Katarina
For last week’s practice question, we quizzed participants on RT forgetting their insulin, and what would be the best response. 63.10% of respondents chose the best answer. We want to clarify and share this important information, so you can pass it on to people living with diabetes and your colleagues, plus prepare for exam success!
Before we start though, if you don’t want any spoilers and haven’t tried the question yet, you can answer it below: Answer Question

RT has type two diabetes and has been maintaining a time and range of 70% or greater. However, when they show up at the office, the last week’s time in range dropped to 30%. You ask what was different this week from the previous few months. RT tells you they went on a five day fishing trip and forgot their insulin.
What’s the best response?
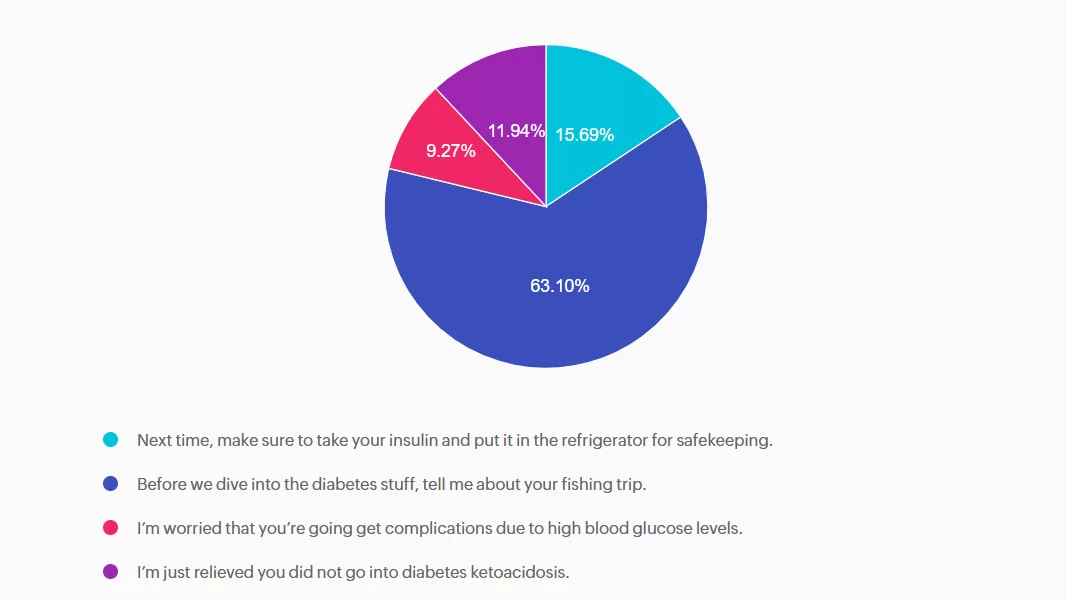
Answer A is incorrect: 15.69% chose this answer, “Next time, make sure to take your insulin and put it in the refrigerator for safekeeping.” This approach goes under the compliance model, where the healthcare professional only provides one way instruction without considering the individuals insights and problem solving skills. We want to work toward a person-centered collaborative approach to foster connection.
Answer B is correct: 63.10% chose this answer, “Before we dive into the diabetes stuff, tell me about your fishing trip.” Great job! This is the best answer. By asking RT about their fishing trip first, you let them know you are interested in their life experiences and this helps to establish a connection. After hearing about the trip, we might pivot and say something like, “Do you want to discuss strategies to bring your insulin on your next fishing trip?”
Answer C is incorrect: 9.27% chose this answer, “I’m worried that you’re going get complications due to high blood glucose levels.” Although this statement shows concern, it is unlikely that RT will get diabetes complications from not taking their insulin for a few days. This statement could lead to feelings of shame and failure, and may close the door to making a meaningful connection.
Answer D is incorrect: 11.94% chose this answer, “I’m just relieved you did not go into diabetes ketoacidosis.” This statement could evoke feelings of guilt and shame, that could close the door to future communication. And if RT has type 2 diabetes, the chance of DKA is minimal. Instead of focusing on the HCP feelings, let’s check in with RT and explore problem solving strategies for future trips that would work for them.
We hope you appreciate this week’s rationale! Thank you so much for taking the time to answer our Question of the Week and participate in this fun learning activity!

According to the latest CDC Data, over 16% of Americans are living with diabetes and 38% have prediabetes. This means about half of our communities are living with hyperglycemia.
Advocacy and education play essential roles in diabetes care and prevention. By equipping individuals with knowledge about diabetes management, healthy lifestyle choices, and preventative measures, we empower them to take ownership of their health and inspire change within their communities.
Community-centered education can be incredibly powerful—when people feel informed and supported, they’re more likely to make meaningful changes and encourage others to do the same. This creates a ripple effect, fostering healthier communities and potentially reducing the prevalence of diabetes over time.
Wear blue: Wear blue on World Diabetes Day (November 14th) and throughout the month. You can also display a blue circle symbol in your window.
Participate in events: Join a Global Diabetes Walk or create your own. Support local chapter events hosted by organizations like the American Diabetes Association or Breakthrough T1D.
Host an event: Organize a fundraising event like a farm fresh sale or car wash, or host an educational session like a “Lunch and Learn” with a local expert.
Spread the word: Share educational content, personal stories, and facts about diabetes on social media, You can also share information via email or newsletters.
Post the Diabetes Risk test: Post the American Diabetes Association Risk Test (see below) in your organization’s or community’s newsletter.
We have put together a list of FREE Webinars and diabetes resources in English and Spanish to share with people living with prediabetes and diabetes. Thank you for your advocacy and belief that we can make a difference.
ADA’s Diabetes Food Hub – English and Spanish! Web site filled with information on healthy eating and an abundance of delicious recipes.
ADA Resources in Spanish – this newly opened information hub is perfect for those who prefer to learn and read in Spanish.
ADA’s FREE Life with Diabetes Program: ADA’s program includes six digital, printable journeys to teach how to live well with diabetes; a monthly e-newsletter with tips, stories, and more resources; six free issues of the Diabetes Forecast® magazine; access to an online community and local events. (The program is available in both English and Spanish).
ADA’s Risk Quiz: 60-second online risk assessment for type 2 diabetes. ADA created a self-assessment and a version to fill out the assessment for others. There’s also a printable version in English & Spanish that can be distributed to help ascertain risk. This is a great first step in helping individuals consider coming in for an appointment
CDC Diabetes Prevention Program Curricula and Handouts This site offers excellent resources for those interested in offering Diabetes Prevention Education in English and Spanish.
National Diabetes Education Program is an online library of resources compiled by the NDEP to help provide accurate information and support for people living with prediabetes and diabetes.
Spanish Language Resources: language can be a barrier to adequate and quality care. ADCES has created a number of free downloads for people with diabetes and prediabetes, which have been translated into Spanish.
Type 1 Diabetes Resource Page – Includes is a list of helpful online resources for Type 1 Diabetes. It include sites for national organizations like the American Diabetes Association (ADA), sites for diabetes interest groups, and other participant organizations that provide helpful diabetes tips and opportunities to join online groups.
Panther Diabetes Technology Deciphered. Get to the gist of what you need to know. Essential resources and guidance for health care professionals working with diabetes technology.
DiabetesWisePro for Clinicians A non-biased web site for health care professionals that has a quick tool to access insurance coverage information, how to order devices, what to include and where to go for support.
DiabetesWise A non-biased website that helps people with diabetes learn about different diabetes devices and determine the best match for their needs
Insulin Cost Savings Toolkit Resource Page – An ADCES complete listing of low cost insulin options and resources.
Technology Cost Savings Resource Page – An ADCES listing of websites and information to obtain pumps and sensors for a lower cost.
Cheat Sheets: We have assembled an abundance of helpful diabetes education cheat sheets for healthcare professionals and those living with diabetes. Feel free to print and share!

Join our special guest speaker, Nick Kundrat, and join the conversation!
Beyond Blood Glucose: Empowering Health Through a Holistic Lens
November 19th at 11:30 AM PST

MT is a 29-year-old with Type 1 diabetes who is currently 14 weeks pregnant. She uses a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) with concurrent fingersticks and uploads her glucose data weekly. Her CGM settings was already set to the recommended time in range and the latest CGM report shows the following: time in range (TIR): 67%, time below range: 6%, time above range: 27%.
Based on current ADA Standard of Care, which of the following statements is most accurate regarding her CGM values?

Level 5 | Beyond Blood Glucose: Empowering Health Through a Holistic Lens with:
Speaker Nick Kundrat, BS, CEP, CDCES, LMT
Use the code Cyber30 for 30% off at checkout!